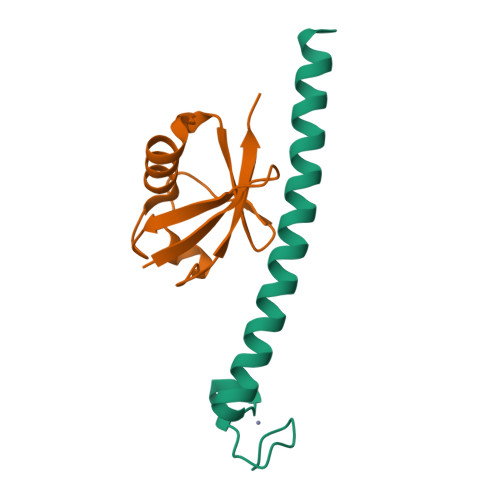
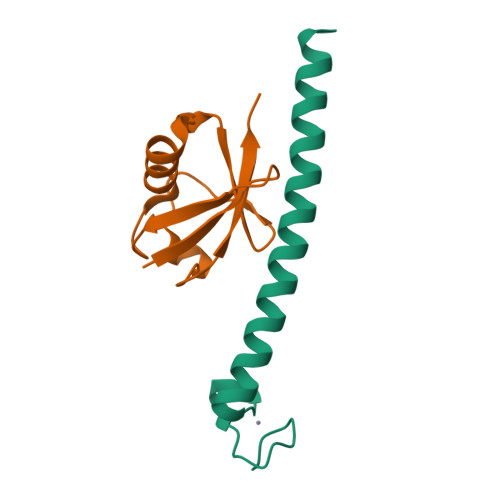
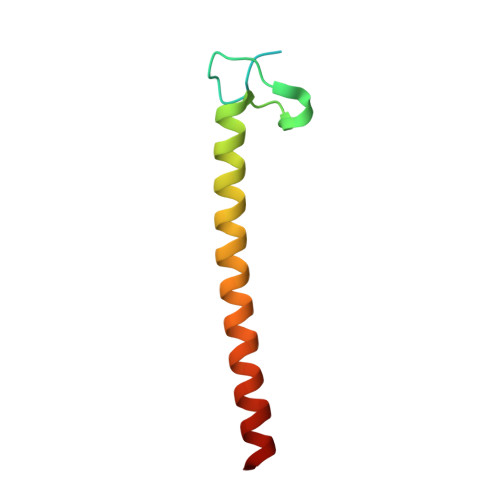
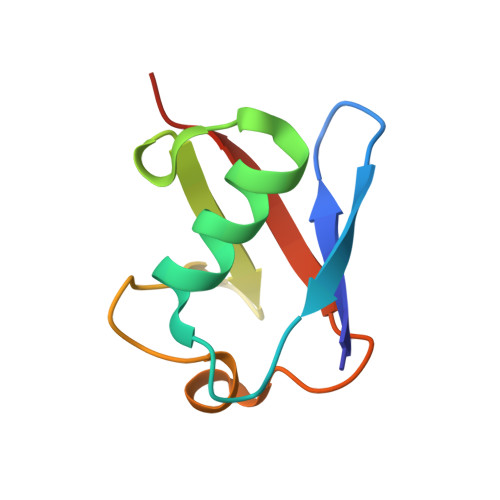
Crystal structure of the ubiquitin binding domains of rabex-5 reveals two modes of interaction with ubiquitin.
Penengo, L., Mapelli, M., Murachelli, A.G., Confalonieri, S., Magri, L., Musacchio, A., Di Fiore, P.P., Polo, S., Schneider, T.R.(2006) Cell 124: 1183-1195
- PubMed: 16499958
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.020
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2C7M, 2C7N - PubMed Abstract:
The interaction between ubiquitinated proteins and intracellular proteins harboring ubiquitin binding domains (UBDs) is critical to a multitude of cellular processes. Here, we report that Rabex-5, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Rab5, binds to Ub through two independent UBDs. These UBDs determine a number of properties of Rabex-5, including its coupled monoubiquitination and interaction in vivo with ubiquitinated EGFRs. Structural and biochemical characterization of the UBDs of Rabex-5 revealed that one of them (MIU, motif interacting with ubiquitin) binds to Ub with modes superimposable to those of the UIM (ubiquitin-interacting motif):Ub interaction, although in the opposite orientation. The other UBD, RUZ (Rabex-5 ubiquitin binding zinc finger) binds to a surface of Ub centered on Asp58(Ub) and distinct from the "canonical" Ile44(Ub)-based surface. The two binding surfaces allow Ub to interact simultaneously with different UBDs, thus opening new perspectives in Ub-mediated signaling.
Organizational Affiliation:
IFOM, the FIRC Institute for Molecular Oncology Foundation, Via Adamello 16, 20139 Milan, Italy.