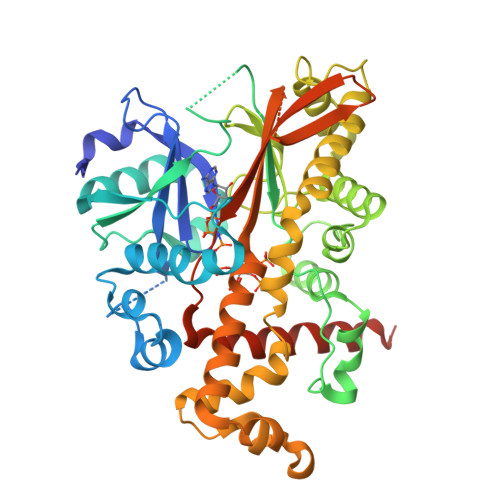
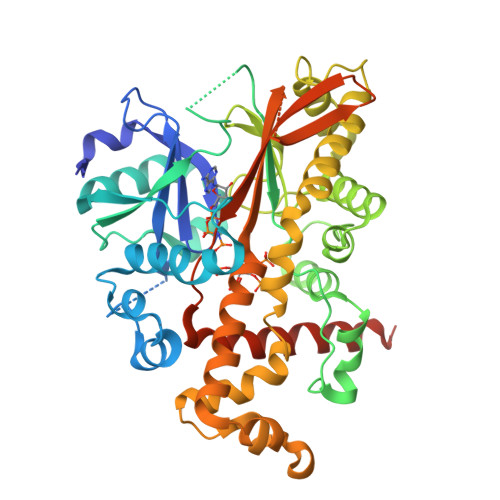
Conformational Changes Undergone by Inositol 1,3,4,5,6-Pentakisphosphate 2-Kinase Upon Substrate Binding: The Role of N-Lobe and Enantiomeric Substrate Preference
Banos-Sanz, J.I., Sanz-Aparicio, J., Whitfield, H., Hamilton, C., Brearley, C.A., Gonzalez, B.(2012) J Biological Chem 287: 29237
- PubMed: 22745128
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.363671
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4AXC, 4AXD, 4AXE, 4AXF - PubMed Abstract:
Inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate 2-kinase (IP(5) 2-K) catalyzes the synthesis of inositol 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexakisphosphate from ATP and IP(5). Inositol 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexakisphosphate is implicated in crucial processes such as mRNA export, DNA editing, and phosphorus storage in plants. We previously solved the first structure of an IP(5) 2-K, which shed light on aspects of substrate recognition. However, failure of IP(5) 2-K to crystallize in the absence of inositide prompted us to study putative conformational changes upon substrate binding. We have made mutations to residues on a region of the protein that produces a clasp over the active site. A W129A mutant allowed us to capture IP(5) 2-K in its different conformations by crystallography. Thus, the IP(5) 2-K apo-form structure displays an open conformation, whereas the nucleotide-bound form shows a half-closed conformation, in contrast to the inositide-bound form obtained previously in a closed conformation. Both nucleotide and inositide binding produce large conformational changes that can be understood as two rigid domain movements, although local changes were also observed. Changes in intrinsic fluorescence upon nucleotide and inositide binding are in agreement with the crystallographic findings. Our work suggests that the clasp might be involved in enzyme kinetics, with the N-terminal lobe being essential for inositide binding and subsequent conformational changes. We also show how IP(5) 2-K discriminates between inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and 3,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate enantiomers and that substrate preference can be manipulated by Arg(130) mutation. Altogether, these results provide a framework for rational design of specific inhibitors with potential applications as biological tools for in vivo studies, which could assist in the identification of novel roles for IP(5) 2-K in mammals.
Organizational Affiliation:
Departamento de Cristalografía y Biología Estructural, Instituto de Química-Física Rocasolano, CSIC, Serrano 119, 28006-Madrid, Spain.