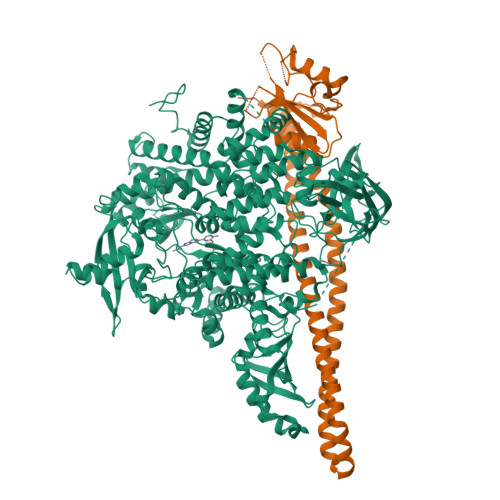
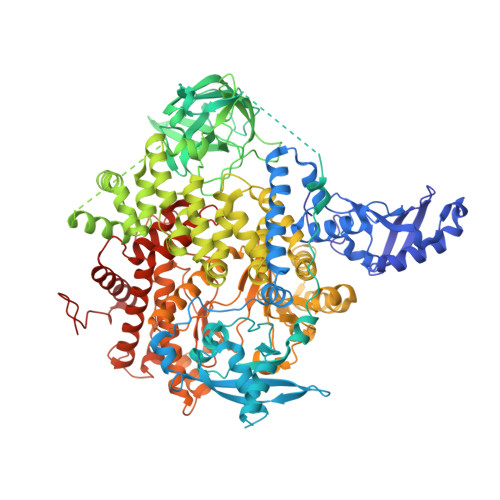
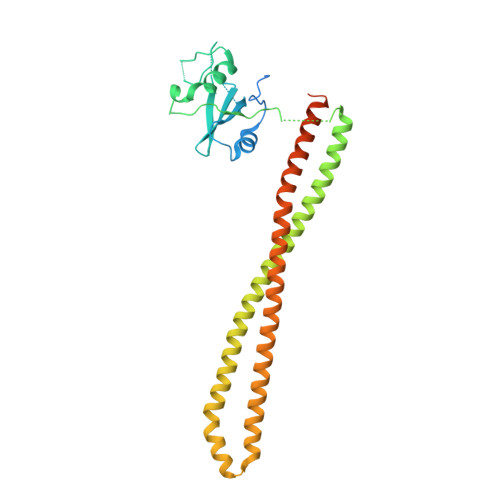
Discovery of imidazo[1,2-a]-pyridine inhibitors of pan-PI3 kinases that are efficacious in a mouse xenograft model.
Han, W., Menezes, D.L., Xu, Y., Knapp, M.S., Elling, R., Burger, M.T., Ni, Z.J., Smith, A., Lan, J., Williams, T.E., Verhagen, J., Huh, K., Merritt, H., Chan, J., Kaufman, S., Voliva, C.F., Pecchi, S.(2016) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 742-746
- PubMed: 26774655
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.01.003
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5FI4 - PubMed Abstract:
Alterations in PI3K/AKT signaling are known to be implicated with tumorigenesis. The PI3 kinases family of lipid kinases has been an attractive therapeutic target for cancer treatment. Imidazopyridine compound 1, a potent, selective, and orally available pan-PI3K inhibitor, identified by scaffold morphing of a benzothiazole hit, was further optimized in order to achieve efficacy in a PTEN-deleted A2780 ovarian cancer mouse xenograft model. With a hypothesis that a planar conformation between the core and the 6-heteroaryl ring will allow for the accommodation of larger 5'-substituents in a hydrophobic area under P-loop, SAR efforts focused on 5'-alkoxy heteroaryl rings at the 6-position of imidazopyridine and imidazopyridazine cores that have the same dihedral angle of zero degrees. 6'-Alkoxy 5'-aminopyrazines in the imidazopyridine series were identified as the most potent compounds in the A2780 cell line. Compound 14 with 1,1,1-trifluoroisopropoxy group at 6'-position demonstrated excellent potency and selectivity, good oral exposure in rats and in vivo efficacy in A2780 tumor-bearing mouse. Also, we disclose the X-ray co-crystal structure of one enantiomer of compound 14 in PI3Kα, confirming that the trifluoromethyl group fits nicely in the hydrophobic hot spot under P-loop.
Organizational Affiliation:
Global Discovery Chemistry, Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research, 5300 Chiron Way, Emeryville, CA 94608, United States.