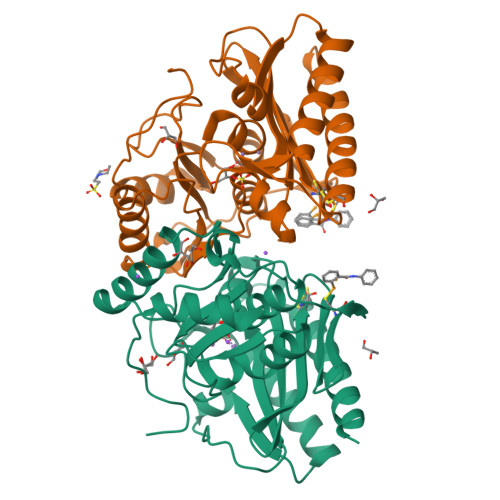
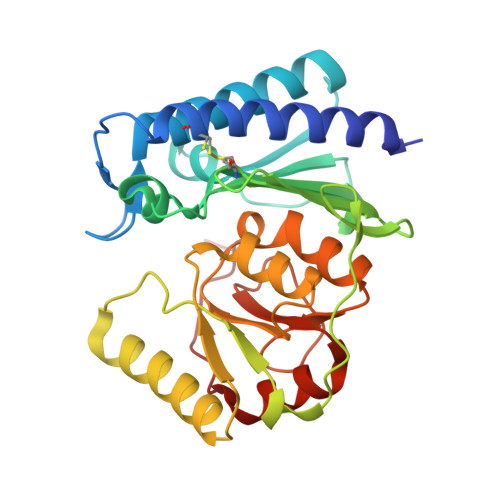
Crystallization and structure of ebselen bound to Cys141 of human inositol monophosphatase.
Fenn, G.D., Waller-Evans, H., Atack, J.R., Bax, B.D.(2020) Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun 76: 469-476
- PubMed: 33006574
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X20011310
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6ZK0 - PubMed Abstract:
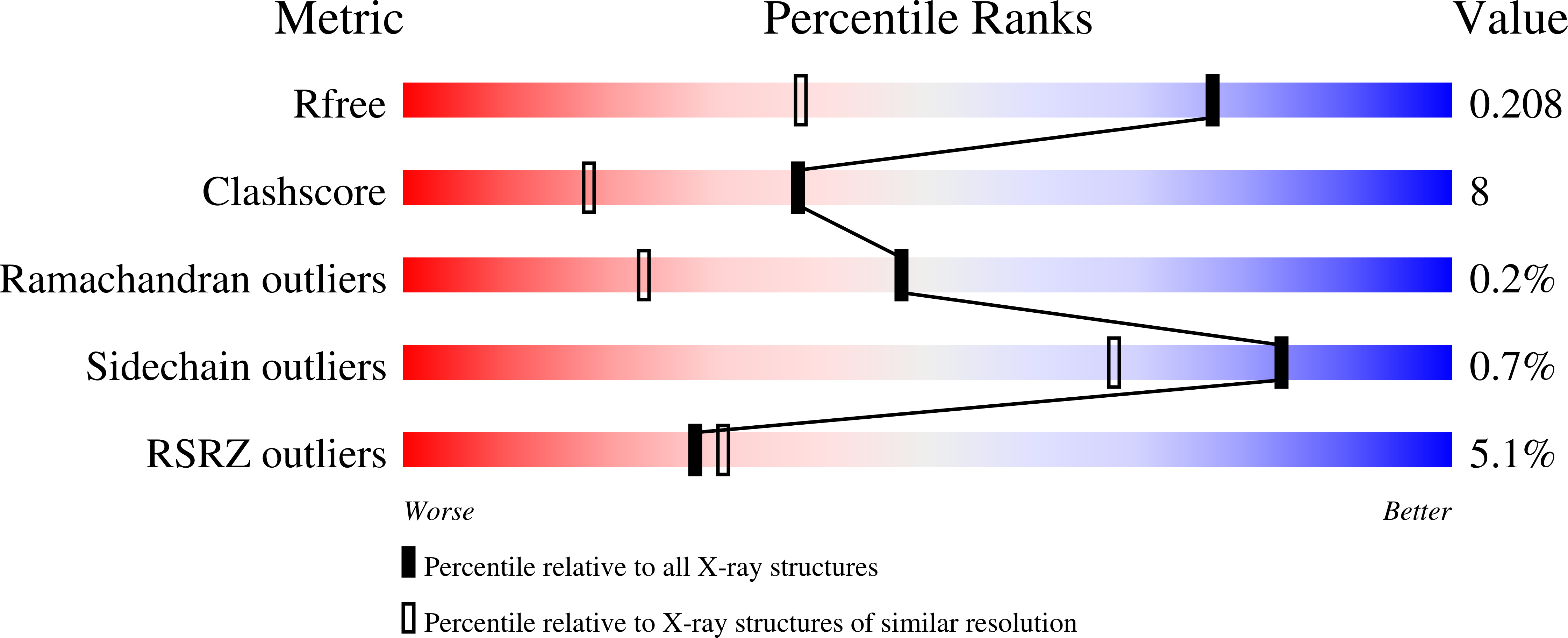
Inositol monophosphatase (IMPase) is inhibited by lithium, which is the most efficacious treatment for bipolar disorder. Several therapies have been approved, or are going through clinical trials, aimed at the replacement of lithium in the treatment of bipolar disorder. One candidate small molecule is ebselen, a selenium-containing antioxidant, which has been demonstrated to produce lithium-like effects both in a murine model and in clinical trials. Here, the crystallization and the first structure of human IMPase covalently complexed with ebselen, a 1.47 Å resolution crystal structure (PDB entry 6zk0), are presented. In the complex with human IMPase, ebselen in a ring-opened conformation is covalently attached to Cys141, a residue located away from the active site. IMPase is a dimeric enzyme and in the crystal structure two adjacent dimers share four ebselen molecules, creating a tetramer with approximate 222 symmetry. In the crystal structure presented in this publication, the active site in the tetramer is still accessible, suggesting that ebselen may function as an allosteric inhibitor or may block the binding of partner proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Medicines Discovery Institute, School of Biosciences, Cardiff University, Cardiff CF10 3AT, United Kingdom.