Characterization of the Stereoselective P450 Enzyme BotCYP Enables the In Vitro Biosynthesis of the Bottromycin Core Scaffold.
Adam, S., Franz, L., Milhim, M., Bernhardt, R., Kalinina, O.V., Koehnke, J.(2020) J Am Chem Soc 142: 20560-20565
- PubMed: 33249843
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c10361
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7ABA, 7ABB - PubMed Abstract:
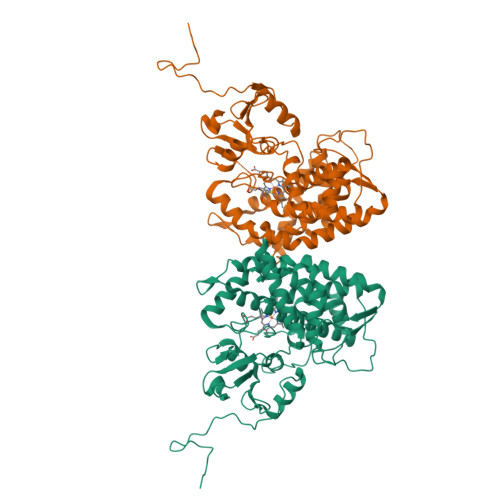
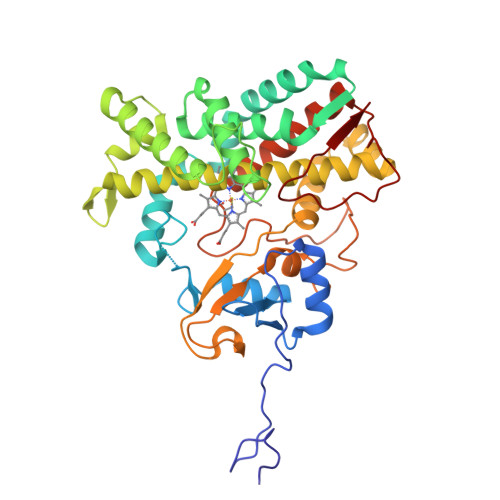
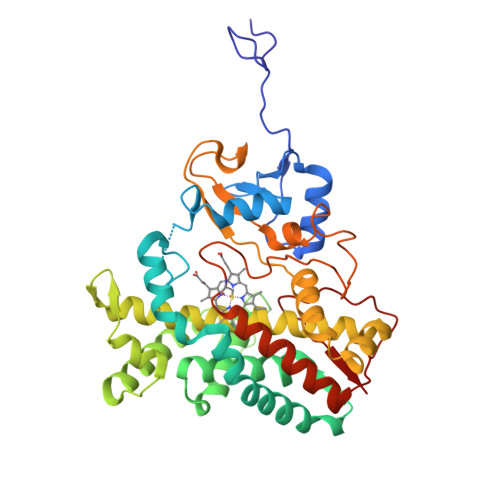
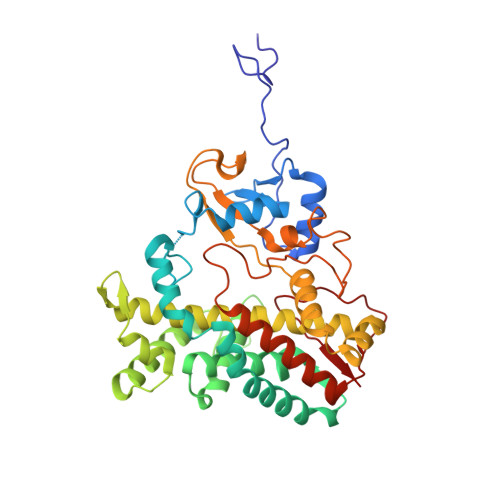
Bottromycins are ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide natural product antibiotics that are effective against high-priority human pathogens such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus . The total synthesis of bottromycins involves at least 17 steps, with a poor overall yield. Here, we report the characterization of the cytochrome P450 enzyme BotCYP from a bottromycin biosynthetic gene cluster. We determined the structure of a close BotCYP homolog and used our data to conduct the first large-scale survey of P450 enzymes associated with RiPP biosynthetic gene clusters. We demonstrate that BotCYP converts a C-terminal thiazoline to a thiazole via an oxidative decarboxylation reaction and provides stereochemical resolution for the pathway. Our data enable the two-pot in vitro production of the bottromycin core scaffold and may allow the rapid generation of bottromycin analogues for compound development.
Organizational Affiliation:
Workgroup Structural Biology of Biosynthetic Enzymes, Helmholtz Institute for Pharmaceutical Research Saarland (HIPS), Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research (HZI), Saarland University, Campus Geb. E8.1, 66123 Saarbrücken, Germany.