Discovery of potent 1,1-diarylthiogalactoside glycomimetic inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa LecA with antibiofilm properties.
Bruneau, A., Gillon, E., Furiga, A., Brachet, E., Alami, M., Roques, C., Varrot, A., Imberty, A., Messaoudi, S.(2022) Eur J Med Chem 247: 115025-115025
- PubMed: 36549118
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.115025
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
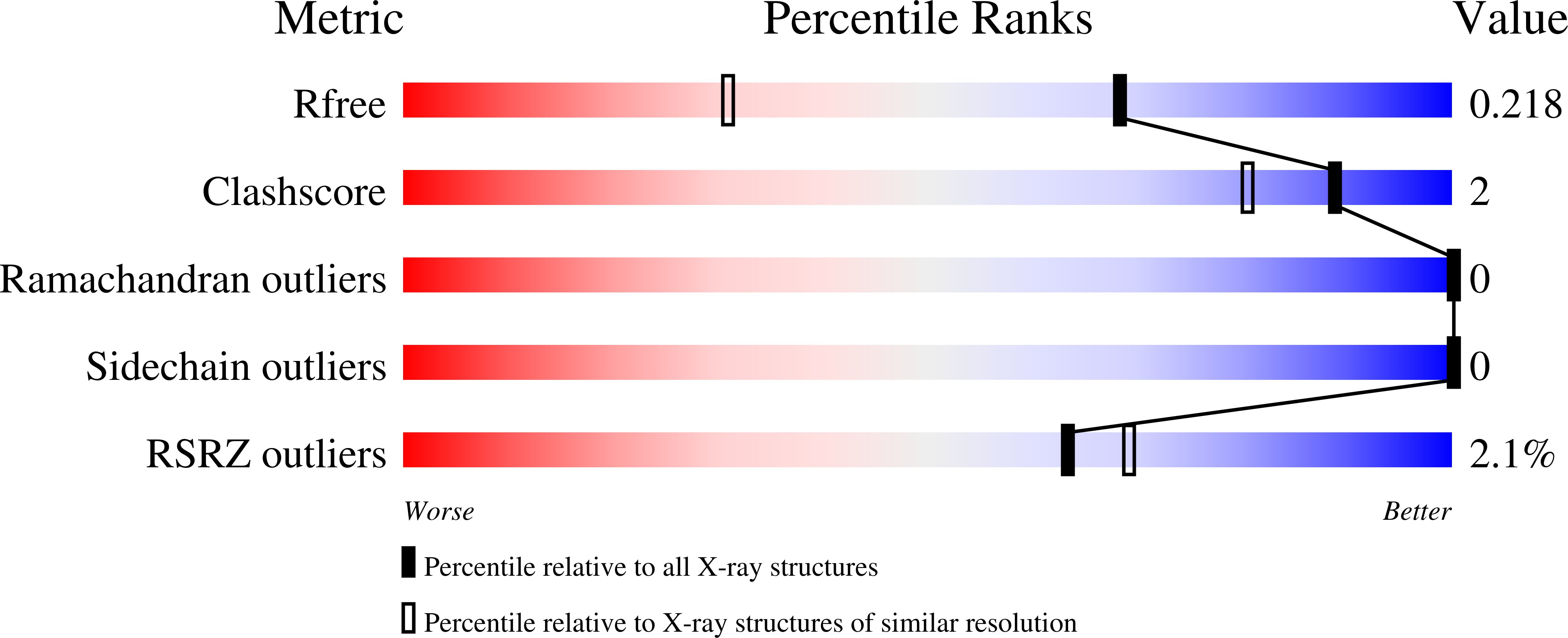
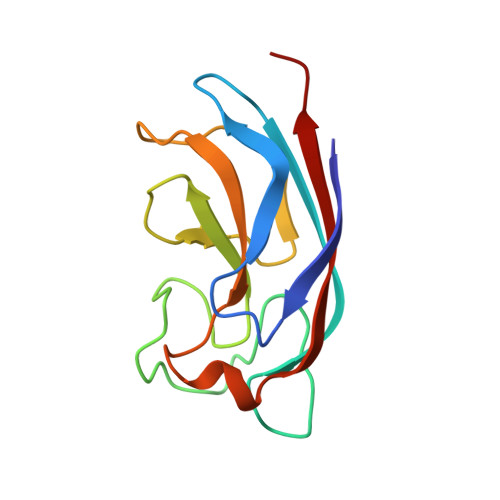
7Z62, 7Z63 - PubMed Abstract:
In this work, β-thiogalactoside mimetics bearing 1,1-diarylmethylene or benzophenone aglycons have been prepared and assayed for their affinity towards LecA, a lectin and virulence factor from Pseudomonas aeruginosa involved in bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation. The hit compound presents higher efficiency than previously described monovalent inhibitors and the crystal structure confirmed the occurrence of additional contacts between the aglycone and the protein surface. The highest affinity (160 nM) was obtained for a divalent ligand containing two galactosides. The monovalent high affinity compound (K d = 1 μM) obtained through structure-activity relationship (SAR) showed efficient antibiofilm activity with no associated bactericidal activity.
Organizational Affiliation:
BioCIS, Univ. Paris-Sud, CNRS, University Paris-Saclay, Châtenay-Malabry, France.