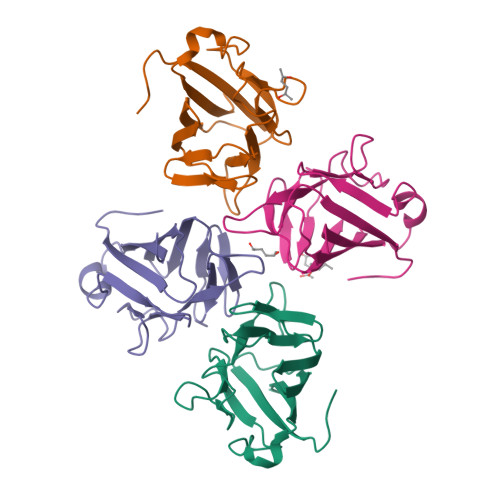
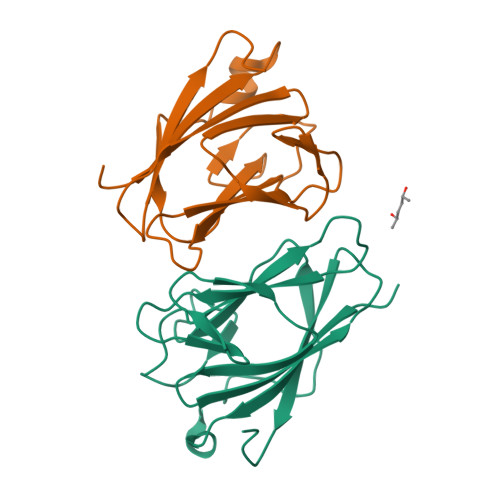
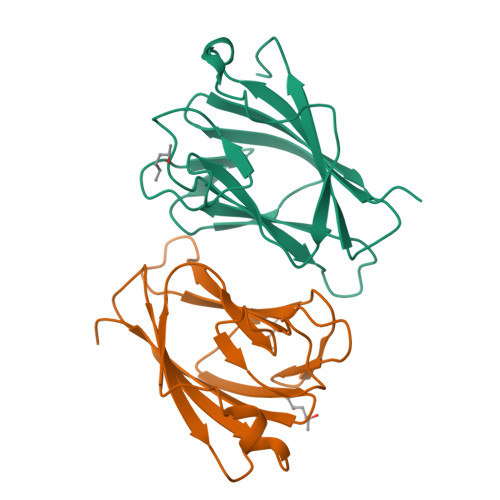
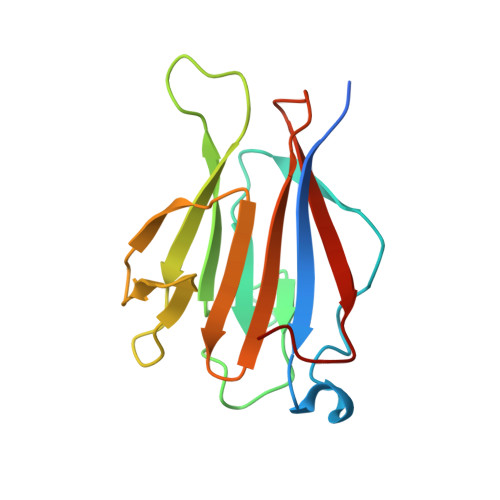
TIFAB regulates the TIFA-TRAF6 signaling pathway involved in innate immunity by forming a heterodimer complex with TIFA.
Nakamura, T., Ohyama, C., Sakamoto, M., Toma, T., Tateishi, H., Matsuo, M., Chirifu, M., Ikemizu, S., Morioka, H., Fujita, M., Inoue, J.I., Yamagata, Y.(2024) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 121: e2318794121-e2318794121
- PubMed: 38442163
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2318794121
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8WWY - PubMed Abstract:
Nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) is activated by various inflammatory and infectious molecules and is involved in immune responses. It has been elucidated that ADP-β-D-manno-heptose (ADP-Hep), a metabolite in gram-negative bacteria, activates NF-κB through alpha-kinase 1 (ALPK1)-TIFA-TRAF6 signaling. ADP-Hep stimulates the kinase activity of ALPK1 for TIFA phosphorylation. Complex formation between phosphorylation-dependent TIFA oligomer and TRAF6 promotes the polyubiquitination of TRAF6 for NF-κB activation. TIFAB, a TIFA homolog lacking a phosphorylation site and a TRAF6 binding motif, is a negative regulator of TIFA-TRAF6 signaling and is implicated in myeloid diseases. TIFAB is indicated to regulate TIFA-TRAF6 signaling through interactions with TIFA and TRAF6; however, little is known about its biological function. We demonstrated that TIFAB forms a complex not with the TIFA dimer, an intrinsic form of TIFA involved in NF-κB activation, but with monomeric TIFA. The structural analysis of the TIFA/TIFAB complex and the biochemical and cell-based analyses showed that TIFAB forms a stable heterodimer with TIFA, inhibits TIFA dimer formation, and suppresses TIFA-TRAF6 signaling. The resultant TIFA/TIFAB complex is a "pseudo-TIFA dimer" lacking the phosphorylation site and TRAF6 binding motif in TIFAB and cannot form the orderly structure as proposed for the phosphorylated TIFA oligomer involved in NF-κB activation. This study elucidated the molecular and structural basis for the regulation of TIFA-TRAF6 signaling by TIFAB.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Kumamoto University, Kumamoto 862-0973, Japan.