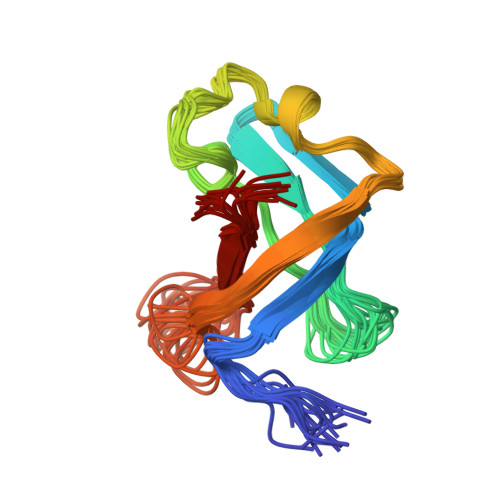
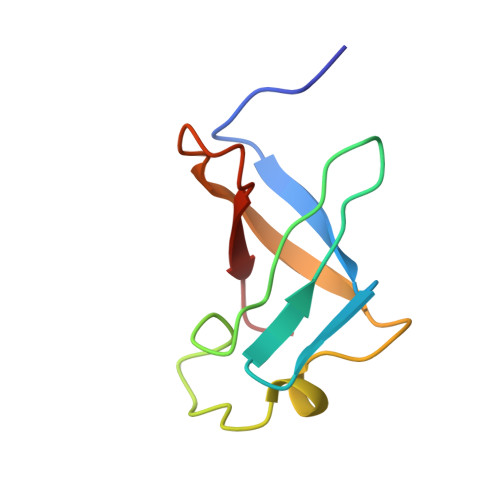
The solution structure of the S1 RNA binding domain: a member of an ancient nucleic acid-binding fold.
Bycroft, M., Hubbard, T.J., Proctor, M., Freund, S.M., Murzin, A.G.(1997) Cell 88: 235-242
- PubMed: 9008164
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81844-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1SRO - PubMed Abstract:
The S1 domain, originally identified in ribosomal protein S1, is found in a large number of RNA-associated proteins. The structure of the S1 RNA-binding domain from the E. coli polynucleotide phosphorylase has been determined using NMR methods and consists of a five-stranded antiparallel beta barrel. Conserved residues on one face of the barrel and adjacent loops form the putative RNA-binding site. The structure of the S1 domain is very similar to that of cold shock protein, suggesting that they are both derived from an ancient nucleic acid-binding protein. Enhanced sequence searches reveal hitherto unidentified S1 domains in RNase E, RNase II, NusA, EMB-5, and other proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of Cambridge, United Kingdom.