Sensing actin dynamics: structural basis for G-actin-sensitive nuclear import of MAL
Hirano, H., Matsuura, Y.(2011) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 414: 373-378
- PubMed: 21964294
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.09.079
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3TPM, 3TPO, 3TPQ - PubMed Abstract:
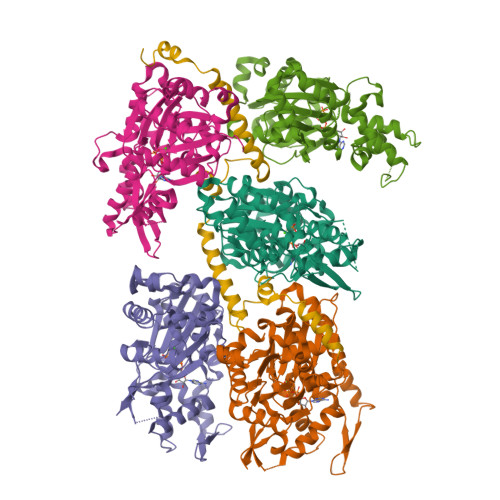
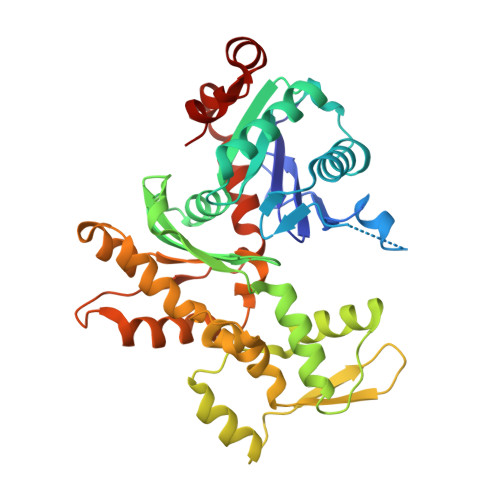
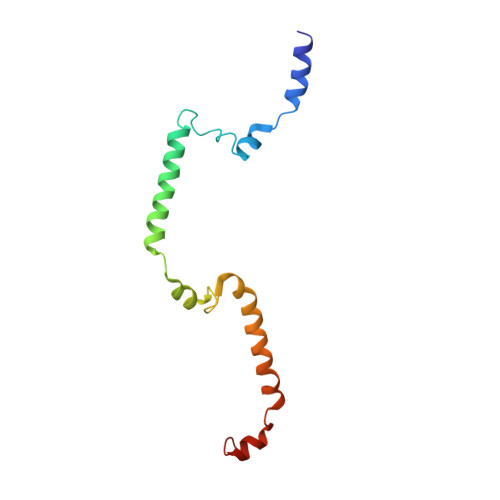
The coordination of cytoskeletal actin dynamics with gene expression reprogramming is emerging as a crucial mechanism to control diverse cellular processes, including cell migration, differentiation and neuronal circuit assembly. The actin-binding transcriptional coactivator MAL (also known as MRTF-A/MKL1/BSAC) senses G-actin concentration and transduces Rho GTPase signals to serum response factor (SRF). MAL rapidly shuttles between the cytoplasm and the nucleus in unstimulated cells but Rho-induced depletion of G-actin leads to MAL nuclear accumulation and activation of transcription of SRF:MAL-target genes. Although the molecular and structural basis of actin-regulated nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of MAL is not understood fully, it is proposed that nuclear import of MAL is mediated by importin α/β heterodimer, and that G-actin competes with importin α/β for the binding to MAL. Here we present structural, biochemical and cell biological evidence that MAL has a classical bipartite nuclear localization signal (NLS) in the N-terminal 'RPEL' domain containing Arg-Pro-X-X-X-Glu-Leu (RPEL) motifs. The NLS residues of MAL adopt an extended conformation and bind along the surface groove of importin-α, interacting with the major- and minor-NLS binding sites. We also present a crystal structure of wild-type MAL RPEL domain in complex with five G-actins. Comparison of the importin-α- and actin-complexes revealed that the binding of G-actins to MAL is associated with folding of NLS residues into a helical conformation that is inappropriate for importin-α recognition.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biology Research Center, Graduate School of Science, Nagoya University, Nagoya 464-8602, Japan.