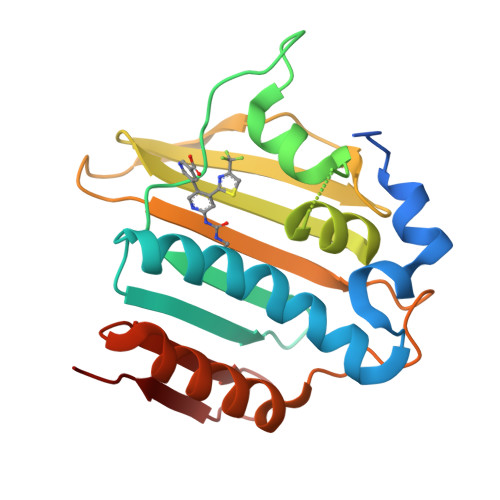
Fragment-to-Hit-to-Lead Discovery of a Novel Pyridylurea Scaffold of ATP Competitive Dual Targeting Type II Topoisomerase Inhibiting Antibacterial Agents.
Basarab, G.S., Manchester, J.I., Bist, S., Boriack-Sjodin, P.A., Dangel, B., Illingworth, R., Sherer, B.A., Sriram, S., Uria-Nickelsen, M., Eakin, A.E.(2013) J Med Chem 56: 8712-8735
- PubMed: 24098982
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm401208b
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4LP0, 4LPB - PubMed Abstract:
The discovery and optimization of a new class of bacterial topoisomerase (DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV) inhibitors binding in the ATP domain are described. A fragment molecule, 1-ethyl-3-(2-pyridyl)urea, provided sufficiently potent enzyme inhibition (32 μM) to prompt further analogue work. Acids and acid isosteres were incorporated at the 5-pyridyl position of this fragment, bridging to a key asparagine residue, improving enzyme inhibition, and leading to measurable antibacterial activity. A CF3-thiazole substituent at the 4-pyridyl position improved inhibitory potency due to a favorable lipophilic interaction. Promising antibacterial activity was seen versus the Gram-positive pathogens Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae and the Gram-negative pathogens Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis . Precursor metabolite incorporation and mutant analysis studies support the mode-of-action, blockage of DNA synthesis by dual target topoisomerase inhibition. Compound 35 was efficacious in a mouse S. aureus disease model, where a 4.5-log reduction in colony forming units versus control was demonstrated.
Organizational Affiliation:
Infection Innovative Medicines, AstraZeneca R&D Boston , 35 Gatehouse Drive, Waltham, Massachusetts 02451, United States.