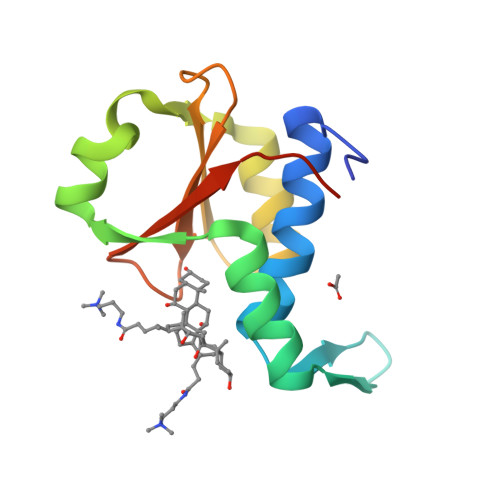
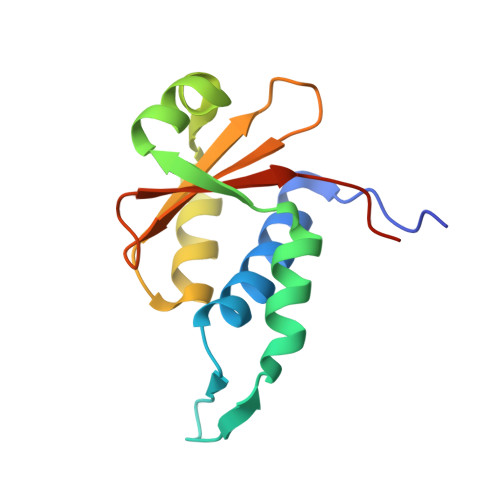
Crystal structure of the EnvZ periplasmic domain with CHAPS.
Hwang, E., Cheong, H.K., Kim, S.Y., Kwon, O., Blain, K.Y., Choe, S., Yeo, K.J., Jung, Y.W., Jeon, Y.H., Cheong, C.(2017) FEBS Lett 591: 1419-1428
- PubMed: 28423182
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12658
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5XGA - PubMed Abstract:
Bacteria sense and respond to osmolarity through the EnvZ-OmpR two-component system. The structure of the periplasmic sensor domain of EnvZ (EnvZ-PD) is not available yet. Here, we present the crystal structure of EnvZ-PD in the presence of CHAPS detergent. The structure of EnvZ-PD shows similar folding topology to the PDC domains of PhoQ, DcuS, and CitA, but distinct orientations of helices and β-hairpin structures. The CD and NMR spectra of EnvZ-PD in the presence of cholate, a major component of bile salts, are similar to those with CHAPS. Chemical cross-linking shows that the dimerization of EnvZ-PD is significantly inhibited by the CHAPS and cholate. Together with β-galactosidase assay, these results suggest that bile salts may affect the EnvZ structure and function in Escherichia coli.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Bioconvergence Analysis, Korea Basic Science Institute (KBSI), Chungbuk, Korea.