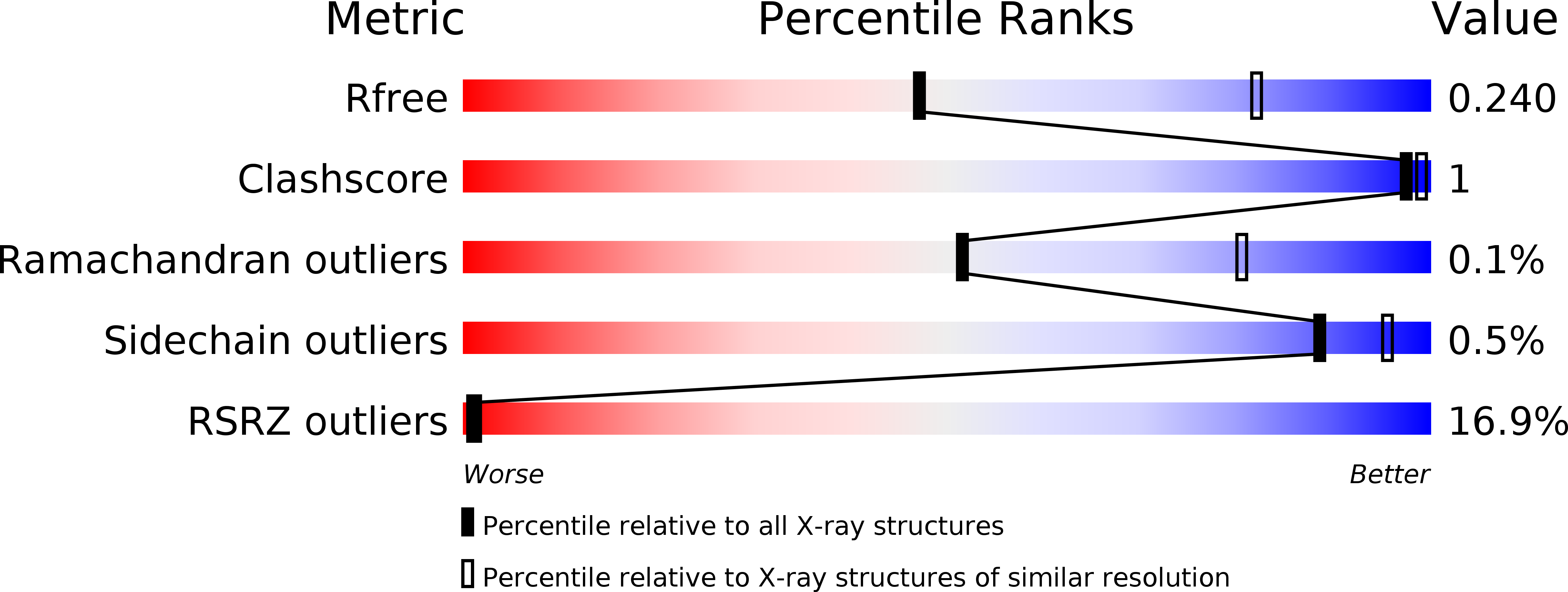
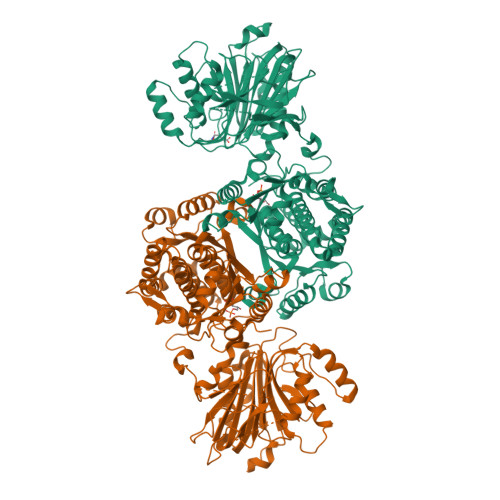
Protein kinase A controls the hexosamine pathway by tuning the feedback inhibition of GFAT-1.
Ruegenberg, S., Mayr, F.A.M.C., Atanassov, I., Baumann, U., Denzel, M.S.(2021) Nat Commun 12: 2176-2176
- PubMed: 33846315
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-22320-y
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6ZMJ, 6ZMK, 7NDL - PubMed Abstract:
The hexosamine pathway (HP) is a key anabolic pathway whose product uridine 5'-diphospho-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) is an essential precursor for glycosylation processes in mammals. It modulates the ER stress response and HP activation extends lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. The highly conserved glutamine fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase 1 (GFAT-1) is the rate-limiting HP enzyme. GFAT-1 activity is modulated by UDP-GlcNAc feedback inhibition and via phosphorylation by protein kinase A (PKA). Molecular consequences of GFAT-1 phosphorylation, however, remain poorly understood. Here, we identify the GFAT-1 R203H substitution that elevates UDP-GlcNAc levels in C. elegans. In human GFAT-1, the R203H substitution interferes with UDP-GlcNAc inhibition and with PKA-mediated Ser205 phosphorylation. Our data indicate that phosphorylation affects the interactions of the two GFAT-1 domains to control catalytic activity. Notably, Ser205 phosphorylation has two discernible effects: it lowers baseline GFAT-1 activity and abolishes UDP-GlcNAc feedback inhibition. PKA controls the HP by uncoupling the metabolic feedback loop of GFAT-1.
Organizational Affiliation:
Max Planck Institute for Biology of Ageing, Cologne, Germany.