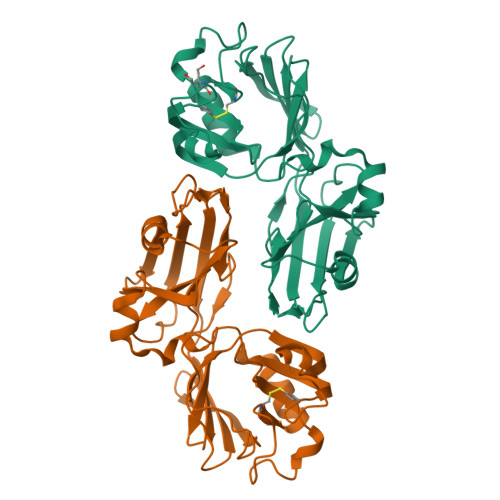
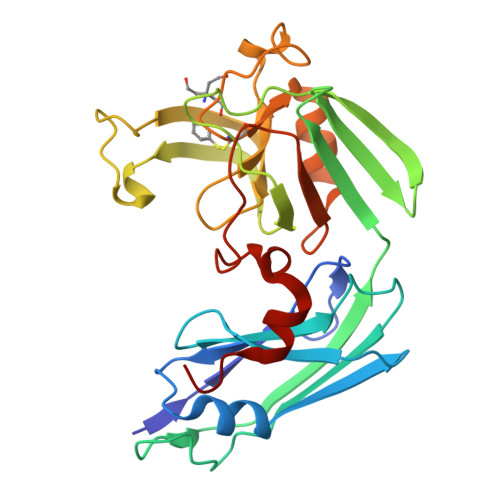
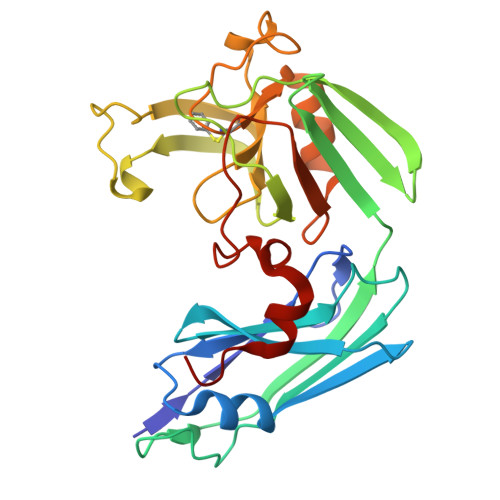
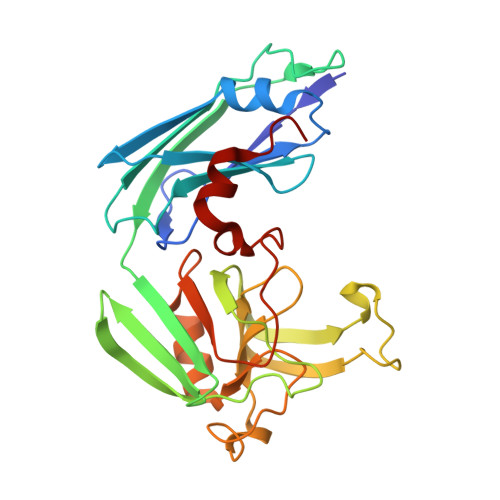
N-Thio-beta-lactams targeting L,D-transpeptidase-2, with activity against drug-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Martelli, G., Pessatti, T.B., Steiner, E.M., Cirillo, M., Caso, C., Bisognin, F., Landreh, M., Monte, P.D., Giacomini, D., Schnell, R.(2021) Cell Chem Biol 28: 1321
- PubMed: 33826941
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2021.03.008
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7A0Z, 7A10, 7A11, 7A1C, 7A1E - PubMed Abstract:
Effective treatment of tuberculosis is frequently hindered by the emerging antimicrobial resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The present study evaluates monocyclic β-lactam compounds targeting the mycobacterial cell wall remodeling. Novel N-thio-β-lactams were designed, synthesized, and characterized on the L,D-transpeptidase-2, a validated target in M. tuberculosis. The candidates were evaluated in biochemical assays identifying five compounds presenting target-specific kinetic constants equal or superior to meropenem, a carbapenem currently considered for tuberculosis therapy. Mass spectrometry in line with the crystal structures of five target-ligand complexes revealed that the N-thio-β-lactams act via an unconventional mode of adduct formation, transferring the thio-residues from the lactam ring to the active-site cysteine of Ldt Mt2 . The resulting stable adducts lead to a long-term inactivation of the target protein. Finally, the candidates were evaluated in vitro against a drug-susceptible and multidrug-resistant clinical isolates of M. tuberculosis, confirming the antimycobacterial effect of these novel compounds.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry "G. Ciamician", University of Bologna, Via Selmi 2, 40126 Bologna, Italy.