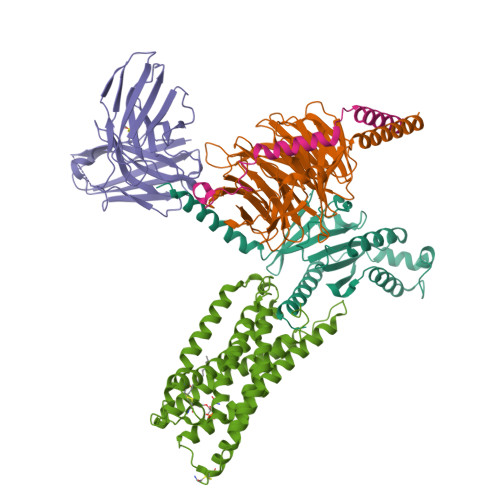
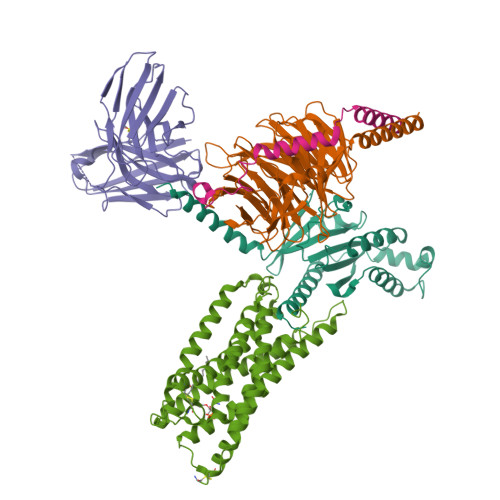
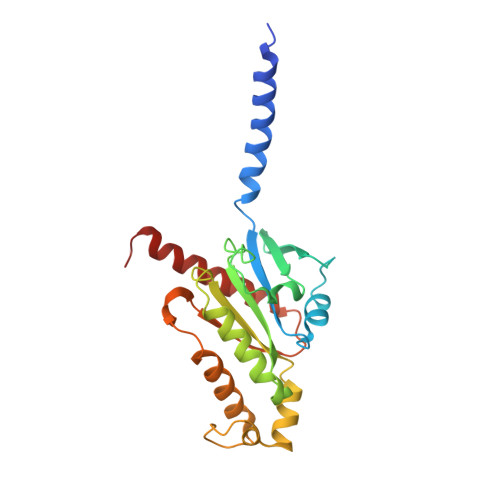
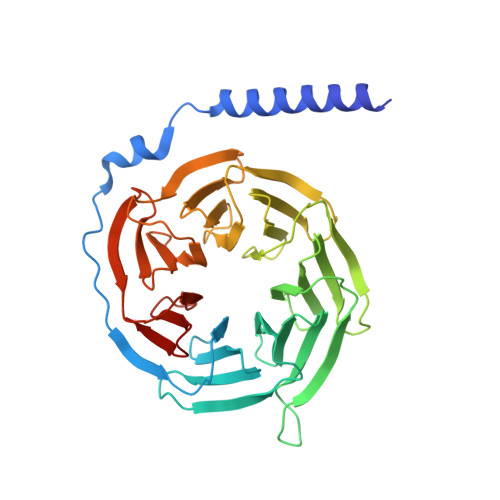
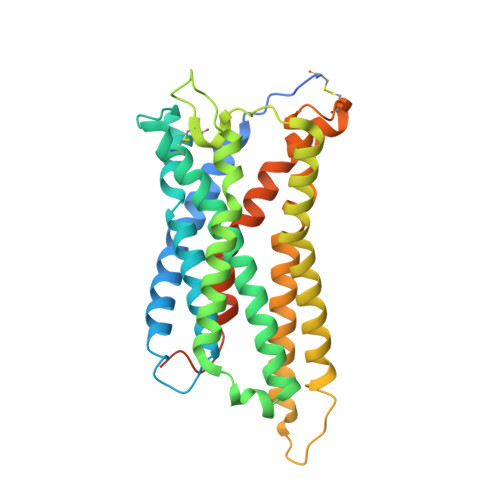
Insights into lysophosphatidylserine recognition and G alpha 12/13 -coupling specificity of P2Y10.
Yin, H., Kamakura, N., Qian, Y., Tatsumi, M., Ikuta, T., Liang, J., Xu, Z., Xia, R., Zhang, A., Guo, C., Inoue, A., He, Y.(2024) Cell Chem Biol 31: 1899-1908.e5
- PubMed: 39265572
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2024.08.005
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8KGG - PubMed Abstract:
The lysophosphatidylserine (LysoPS) receptor P2Y10, also known as LPS 2 , plays crucial roles in the regulation of immune responses and holds promise for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Here, we report the cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of LysoPS-bound P2Y10 in complex with an engineered G 13 heterotrimeric protein. The structure and a mutagenesis study highlight the predominant role of a comprehensive polar network in facilitating the binding and activation of the receptor by LysoPS. This interaction pattern is preserved in GPR174, but not in GPR34. Moreover, our structural study unveils the essential interactions that underlie the Gα 13 engagement of P2Y10 and identifies key determinants for Gα 12 -vs.-Gα 13 -coupling selectivity, whose mutations selectively disrupt Gα 12 engagement while preserving the intact coupling of Gα 13 . The combined structural and functional studies provide insights into the molecular mechanisms of LysoPS recognition and Gα 12/ 13 coupling specificity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Receptor Structure and Signaling, HIT Center for Life Sciences, School of Life Science and Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China.