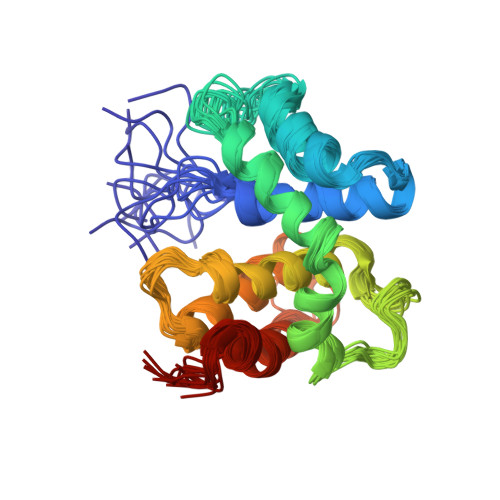
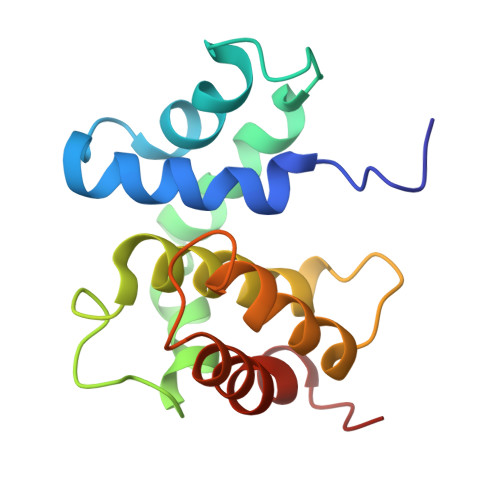
The structure of the transcriptional antiterminator NusB from Escherichia coli.
Altieri, A.S., Mazzulla, M.J., Horita, D.A., Coats, R.H., Wingfield, P.T., Das, A., Court, D.L., Byrd, R.A.(2000) Nat Struct Biol 7: 470-474
- PubMed: 10881193
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/75869
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1EY1 - PubMed Abstract:
We have determined the solution structure of NusB, a transcription antitermination protein from Escherichia coli. The structure reveals a novel, all alpha-helical protein fold. NusB mutations that cause a loss of function (NusB5) or alter specificity for RNA targets (NusB101) are localized to surface residues and likely affect RNA-protein or protein-protein interactions. Residues that are highly conserved among homologs stabilize the protein core. The solution structure of E. coli NusB presented here resembles that of Mycobacterium tuberculosis NusB determined by X-ray diffraction, but differs substantially from a solution structure of E. coli NusB reported earlier.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biophysics Laboratory, National Cancer Institute-FCRDC, Frederick, MD 21702, USA.