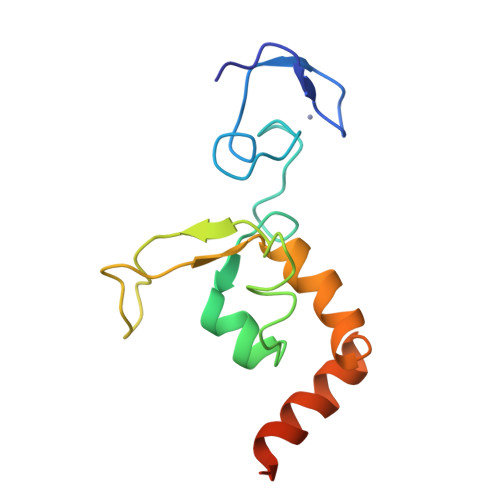
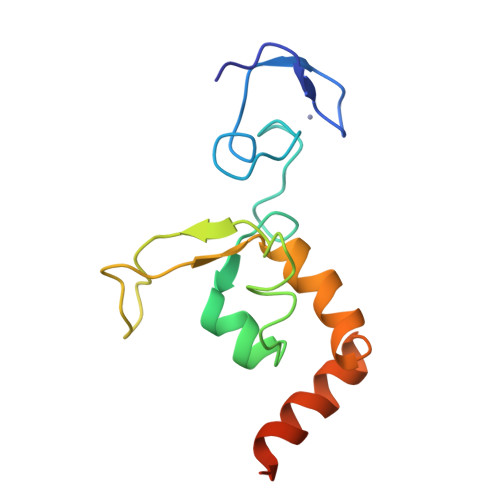
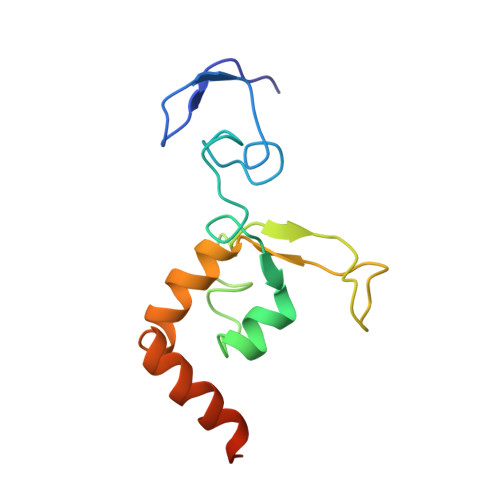
Solution structure of the DNA- and RPA-binding domain of the human repair factor XPA.
Ikegami, T., Kuraoka, I., Saijo, M., Kodo, N., Kyogoku, Y., Morikawa, K., Tanaka, K., Shirakawa, M.(1998) Nat Struct Biol 5: 701-706
- PubMed: 9699634
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1400
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1XPA - PubMed Abstract:
The solution structure of the central domain of the human nucleotide excision repair protein XPA, which binds to damaged DNA and replication protein A (RPA), was determined by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The central domain consists of a zinc-containing subdomain and a C-terminal subdomain. The zinc-containing subdomain has a compact globular structure and is distinct from the zinc-fingers found in transcription factors. The C-terminal subdomain folds into a novel alpha/beta structure with a positively charged superficial cleft. From the NMR spectra of the complexes, DNA and RPA binding surfaces are suggested.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Biological Sciences, Nara Institute of Sciences and Technology, Ikoma, Japan.