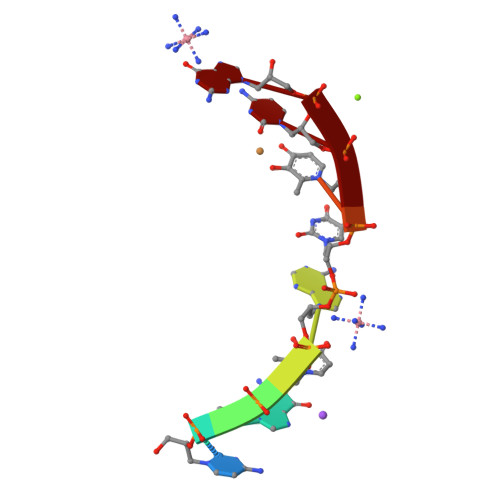
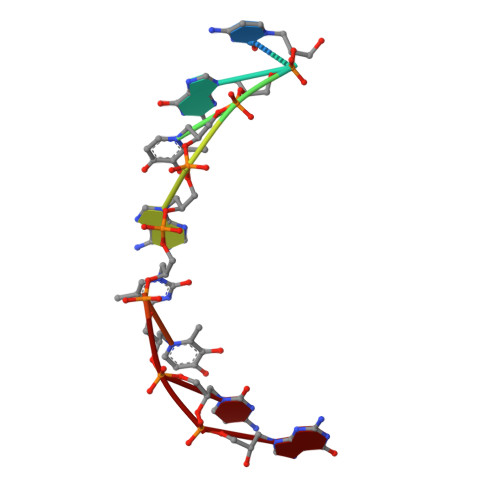
Duplex Structure of a Minimal Nucleic Acid.
Schlegel, M.K., Essen, L.-O., Meggers, E.(2008) J Am Chem Soc 130: 8158
- PubMed: 18529005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja802788g
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2JJA - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of an 8-mer (S)-GNA duplex is presented. As a tool for phasing, the anomalous diffraction of two copper(II) ions within two artificial metallo-base pairs was employed. The duplex structure confirms a canonical Watson-Crick base pairing scheme of GNA with antiparallel strands. The duplex secondary structure is distinct from canonical A- and B-form nucleic acids and can be described as a right-handed helical ribbon wrapped around the helix axis, resulting in a large hollow core. Most intriguingly, neighboring base pairs slide strongly against each other, resulting in extensive interstrand base-base hydrophobic interactions along with unusual hydrophobic intrastrand interactions of nucleobases with their backbone. These results reveal how a minimal nucleic acid backbone can support highly stable Watson-Crick-like duplex formation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Fachbereich Chemie, Philipps-Universität Marburg, Hans-Meerwein Strasse, D-35043 Marburg, Germany.