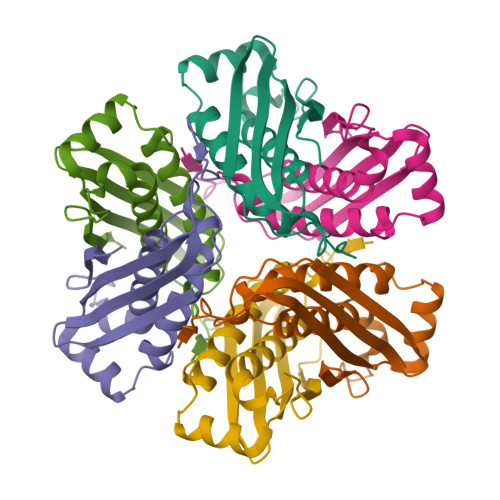
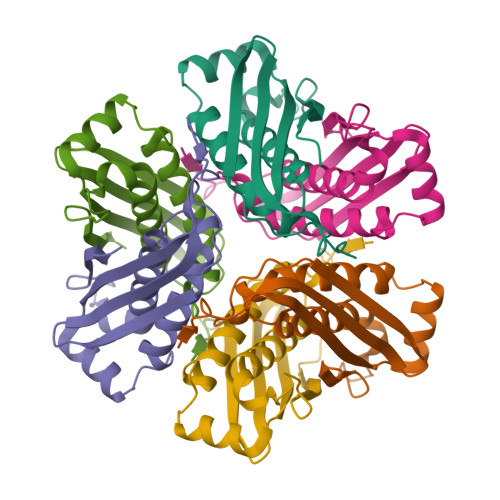
Structure of a putative molybdenum-cofactor biosynthesis protein C (MoaC) from Sulfolobus tokodaii (ST0472)
Yoshida, H., Yamada, M., Kuramitsu, S., Kamitori, S.(2008) Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 64: 589-592
- PubMed: 18607082
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S174430910801590X
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2OHD - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of a putative molybdenum-cofactor (Moco) biosynthesis protein C (MoaC) from Sulfolobus tokodaii (ST0472) was determined at 2.2 A resolution. The crystal belongs to the monoclinic space group C2, with unit-cell parameters a = 123.31, b = 78.58, c = 112.67 A, beta = 118.1 degrees . The structure was solved by molecular replacement using the structure of Escherichia coli MoaC as the probe model. The asymmetric unit is composed of a hexamer arranged as a trimer of dimers with noncrystallographic 32 symmetry. The structure of ST0472 is very similar to that of E. coli MoaC; however, in the ST0472 protein an additional loop formed by the insertion of seven residues participates in intermonomer interactions and the new structure also reveals the formation of an interdimer beta-sheet. These features may contribute to the stability of the oligomeric state.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Structural Biology, Life Science Research Center and Faculty of Medicine, Kagawa University, 1750-1 Ikenobe, Miki-cho, Kita-gun, Kagawa 761-0793, Japan.