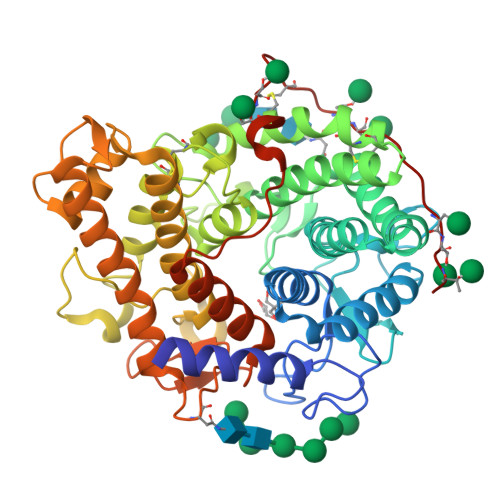
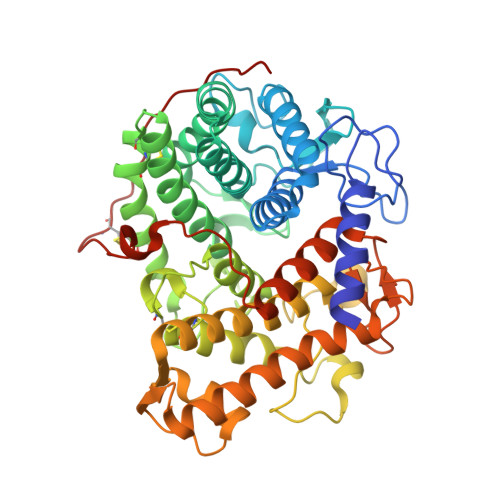
Structure of the catalytic domain of glucoamylase from Aspergillus niger.
Lee, J., Paetzel, M.(2011) Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 67: 188-192
- PubMed: 21301084
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1744309110049390
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3EQA - PubMed Abstract:
Glucoamylase from Aspergillus niger is an industrially important biocatalyst that is utilized in the mass production of glucose from raw starch or soluble oligosaccharides. The G1 isoform consists of a catalytic domain and a starch-binding domain connected by a heavily glycosylated linker region. The amino-terminal catalytic domain of the G1 isoform generated by subtilisin cleavage has been crystallized at pH 8.5, which is a significantly higher pH condition than used for previously characterized glucoamylase crystals. The refined structure at 1.9 Å resolution reveals the active site of the enzyme in complex with both Tris and glycerol molecules. The ligands display both unique and analogous interactions with the substrate-binding site when compared with previous structures of homologous enzymes bound to inhibitors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry, Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, British Columbia, Canada.