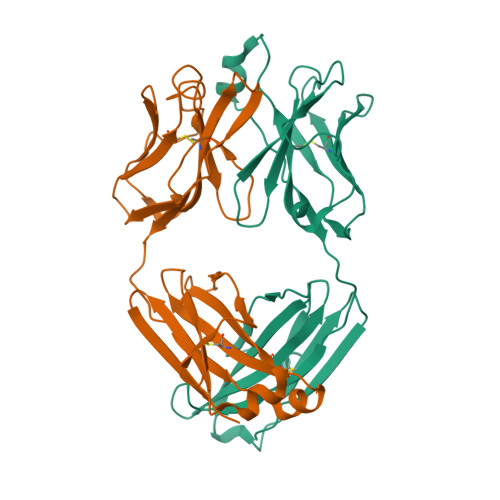
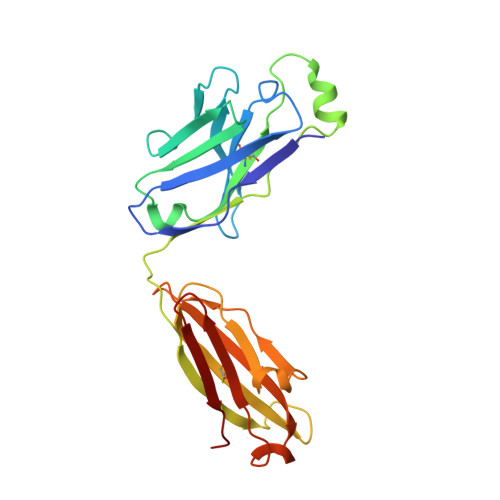
Molecular structure of human GM-CSF in complex with a disease-associated anti-human GM-CSF autoantibody and its potential biological implications.
Blech, M., Seeliger, D., Kistler, B., Bauer, M.M., Hafner, M., Horer, S., Zeeb, M., Nar, H., Park, J.E.(2012) Biochem J 447: 205-215
- PubMed: 22839360
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20120884
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4EOW - PubMed Abstract:
Polyclonal autoantibodies against human GM-CSF (granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor) are a hallmark of PAP (pulmonary alveolar proteinosis) and several other reported autoimmune diseases. MB007 is a high-affinity anti-(human GM-CSF) autoantibody isolated from a patient suffering from PAP which shows only modest neutralization of GM-CSF bioactivity. We describe the first crystal structure of a cytokine-directed human IgG1λ autoantibody-binding fragment (Fab) at 1.9 Å (1 Å=0.1 nm) resolution. Its CDR3-H substantially differs from all VH7 germline IgG1 structures reported previously. We derive a reliable model of the antigen-autoantibody complex by using NMR chemical shift perturbation data in combination with computational methods. Superposition of the modelled complex structure with the human GM-CSF-GM-CSF ternary receptor complex reveals only little overlap between receptor and Fab when bound to GM-CSF. Our model provides a structural basis for understanding the mode of action of the MB007 autoantibody.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Lead Identification and Optimization Support, Structural Research Group, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG, Birkendorfer Strasse 65, 88397 Biberach, Germany. michaela.blech@boehringer-ingelheim.com