Crystal structure of cytochrome P450 CYP105N1 from Streptomyces coelicolor, an oxidase in the coelibactin siderophore biosynthetic pathway
Lim, Y.R., Hong, M.K., Kim, J.K., Doan, T.T., Kim, D.H., Yun, C.H., Chun, Y.J., Kang, L.W., Kim, D.(2012) Arch Biochem Biophys 528: 111-117
- PubMed: 23000034
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2012.09.001
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4FXB - PubMed Abstract:
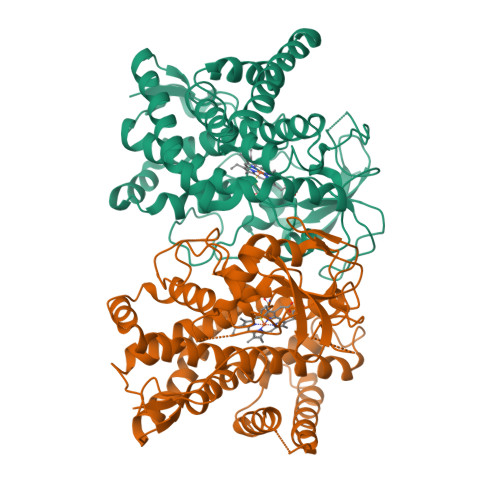
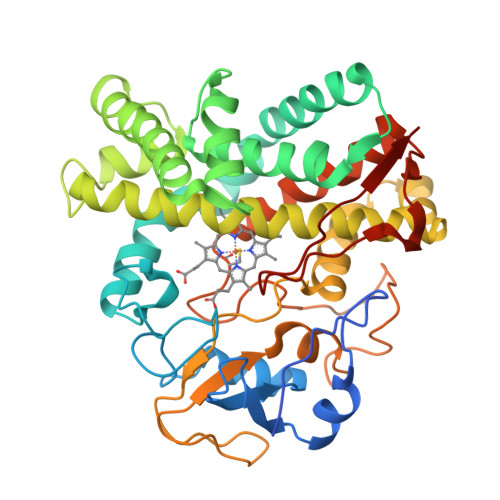
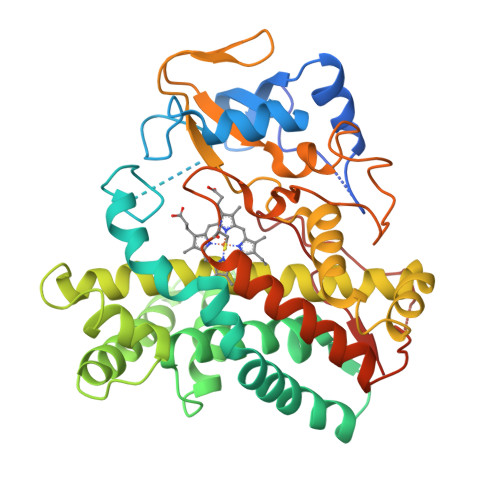
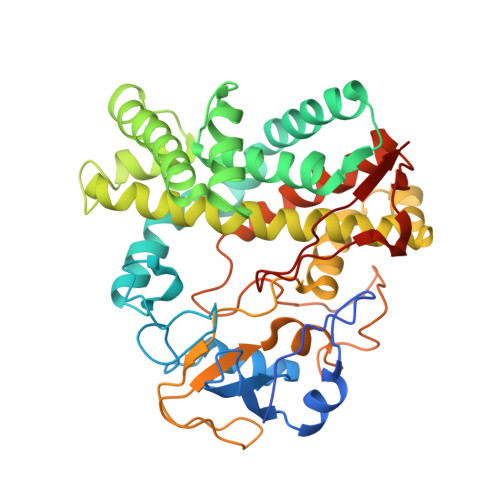
The genome sequence of Streptomyces coelicolor contains 18 cytochrome P450 enzymes. The recombinant CYP105N1 protein has been expressed in Escherichia coli and purified, and we report the biochemical and structural characterization of CYP105N1 from S. coelicolor. The purified protein exhibited the typical CO-binding spectrum of P450 enzymes and type I binding spectra with estradiol and a coelibactin analog. The oxidation of estradiol by CYP105N1, supported by H(2)O(2), produced estriol. The crystal structure of CYP105N1 was determined at 2.9 Å resolution. An unexpected wide open binding pocket located above the heme group was identified, with a volume of approximately 4299 Å(3). These results suggest that the large open pocket to the active site may be a key feature for easy access of the peptidyl carrier protein-bound substrate to perform the hydroxylation reaction. A molecular docking model with coelibactin showed that the phenyl group of coelibactin is located <4 Å away from the heme-iron, suggesting that CYP105N1 may be involved in the hydroxylation of the phenyl ring of the coelibactin precursor during biosynthesis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, Konkuk University, Seoul, Republic of Korea.