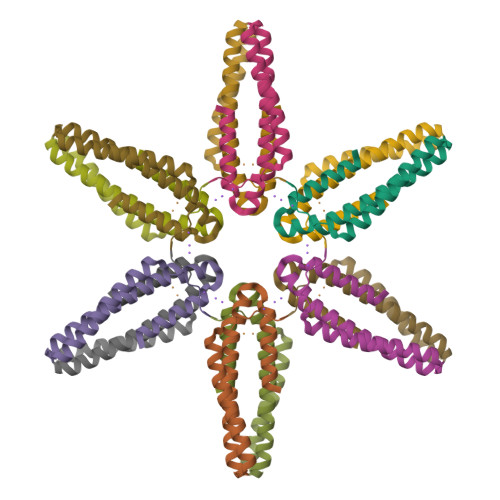
Cu(I)-mediated allosteric switching in a copper-sensing operon repressor (CsoR).
Chang, F.M., Coyne, H.J., Cubillas, C., Vinuesa, P., Fang, X., Ma, Z., Ma, D., Helmann, J.D., Garcia-de los Santos, A., Wang, Y.X., Dann, C.E., Giedroc, D.P.(2014) J Biological Chem 289: 19204-19217
- PubMed: 24831014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.556704
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4M1P - PubMed Abstract:
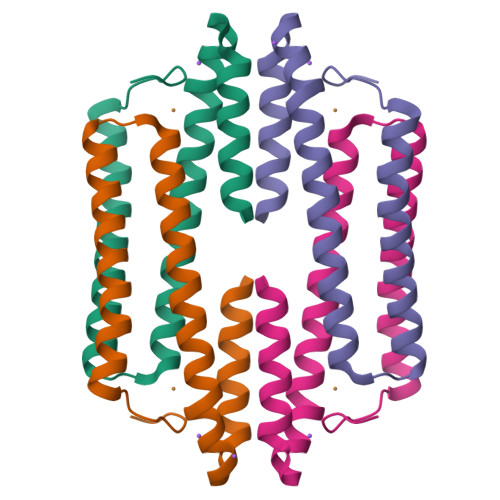
The copper-sensing operon repressor (CsoR) is representative of a major Cu(I)-sensing family of bacterial metalloregulatory proteins that has evolved to prevent cytoplasmic copper toxicity. It is unknown how Cu(I) binding to tetrameric CsoRs mediates transcriptional derepression of copper resistance genes. A phylogenetic analysis of 227 DUF156 protein members, including biochemically or structurally characterized CsoR/RcnR repressors, reveals that Geobacillus thermodenitrificans (Gt) CsoR characterized here is representative of CsoRs from pathogenic bacilli Listeria monocytogenes and Bacillus anthracis. The 2.56 Å structure of Cu(I)-bound Gt CsoR reveals that Cu(I) binding induces a kink in the α2-helix between two conserved copper-ligating residues and folds an N-terminal tail (residues 12-19) over the Cu(I) binding site. NMR studies of Gt CsoR reveal that this tail is flexible in the apo-state with these dynamics quenched upon Cu(I) binding. Small angle x-ray scattering experiments on an N-terminally truncated Gt CsoR (Δ2-10) reveal that the Cu(I)-bound tetramer is hydrodynamically more compact than is the apo-state. The implications of these findings for the allosteric mechanisms of other CsoR/RcnR repressors are discussed.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Department of Chemistry, Indiana University, Bloomington, Indiana 47405-7102.