Fosfomycin Biosynthesis via Transient Cytidylylation of 2-Hydroxyethylphosphonate by the Bifunctional Fom1 Enzyme
Cho, S.H., Kim, S.Y., Tomita, T., Shiraishi, T., Park, J.S., Sato, S., Kudo, F., Eguchi, T., Funa, N., Nishiyama, M., Kuzuyama, T.(2017) ACS Chem Biol 12: 2209-2215
- PubMed: 28727444
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.7b00419
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
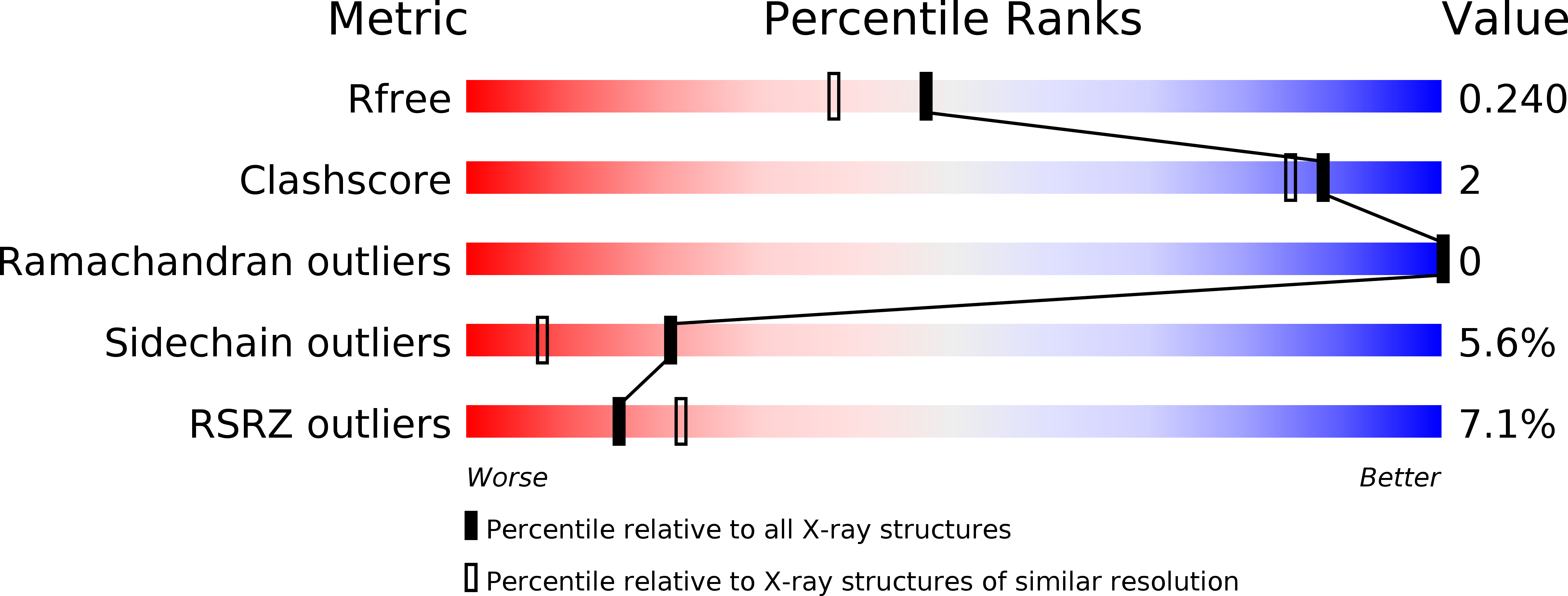
5X3D - PubMed Abstract:
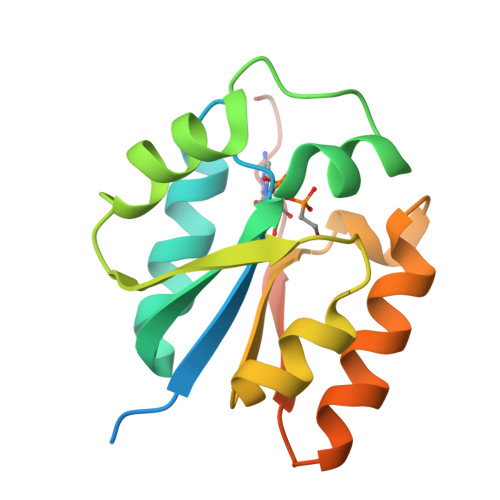
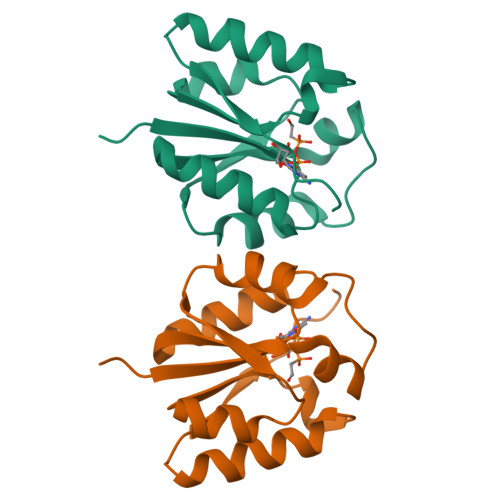
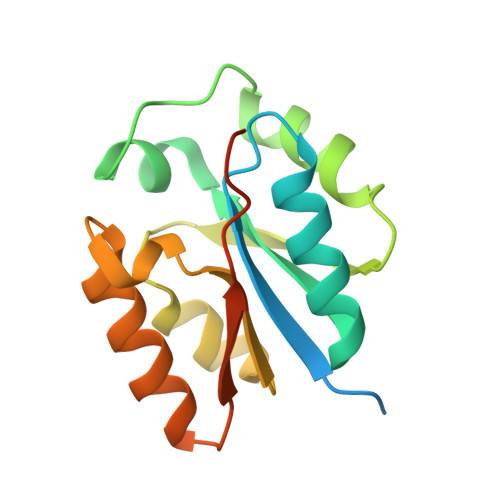
Fosfomycin is a wide-spectrum phosphonate antibiotic that is used clinically to treat cystitis, tympanitis, etc. Its biosynthesis starts with the formation of a carbon-phosphorus bond catalyzed by the phosphoenolpyruvate phosphomutase Fom1. We identified an additional cytidylyltransferase (CyTase) domain at the Fom1 N-terminus in addition to the phosphoenolpyruvate phosphomutase domain at the Fom1 C-terminus. Here, we demonstrate that Fom1 is bifunctional and that the Fom1 CyTase domain catalyzes the cytidylylation of the 2-hydroxyethylphosphonate (HEP) intermediate to produce cytidylyl-HEP. On the basis of this new function of Fom1, we propose a revised fosfomycin biosynthetic pathway that involves the transient CMP-conjugated intermediate. The identification of a biosynthetic mechanism via such transient cytidylylation of a biosynthetic intermediate fundamentally advances the understanding of phosphonate biosynthesis in nature. The crystal structure of the cytidylyl-HEP-bound CyTase domain provides a basis for the substrate specificity and reveals unique catalytic elements not found in other members of the CyTase family.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biotechnology Research Center, The University of Tokyo , 1-1-1 Yayoi, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8657, Japan.