Gene cloning, expression, and X-ray crystallographic analysis of a beta-mannanase from Eisenia fetida.
Ueda, M., Hirano, Y., Fukuhara, H., Naka, Y., Nakazawa, M., Sakamoto, T., Ogata, Y., Tamada, T.(2018) Enzyme Microb Technol 117: 15-22
- PubMed: 30037547
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2018.05.014
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
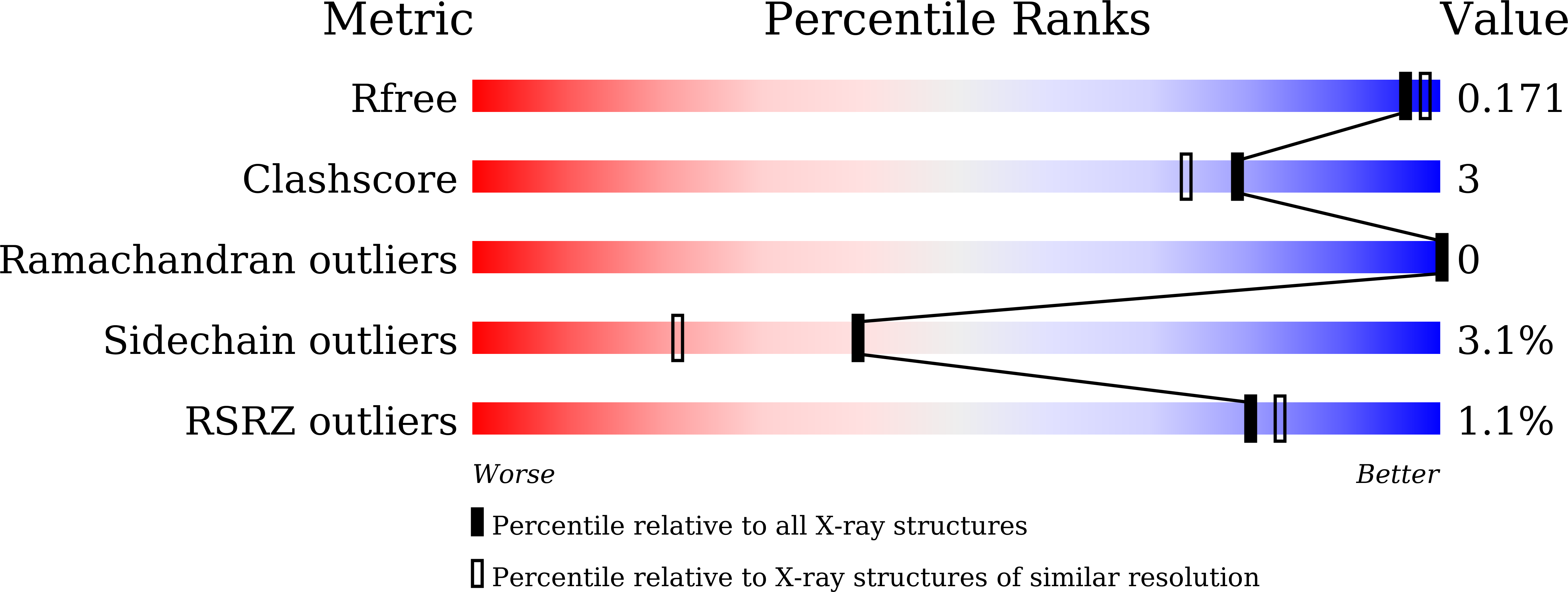
5Y6T - PubMed Abstract:
The endo-1,4-β-mannanases (Ef-Man) gene from Eisenia fetida was determined to consist of 1131 bp and encode a 377 amino acid protein. The amino acid sequence showed similarity with the endo-1,4-β-mannanases of Daphnia pulex (62%), Cryptopygus antarcticus (64%), Crassostrea gigas (61%), Mytilus edulis (60%), and Aplysia kurodai (58%). The gene encoding mature Ef-Man was expressed in Pichia pastoris (GS115 strain). Based on SDS-PAGE analysis, the molecular mass of the purified recombinant Ef-Man (rEf-Man) was estimated to be 39 kDa. All catalytically important residues of endo-1,4-β-mannanases in the glycoside hydrolase (GH) family 5 were conserved in Ef-Man. The optimal temperature for rEf-Man was identified as 60 °C. HPLC and HPAEC analyses suggest that Ef-Man requires at least six subsites for efficient hydrolysis and is capable of performing transglycosylation reactions. The overall structure of rEf-Man is similar to those of GH5 family proteins, and tertiary structures around the active site are conserved among endo-1,4-β-mannanase families. X-ray crystallographic analysis supports the hydrolysis and transglycosylation reaction mechanism determined by HPLC and HPAEC analyses.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Life and Environmental Sciences, Osaka Prefecture University, Osaka, 599-8531, Japan. Electronic address: mueda@biochem.osakafu-u.ac.jp.