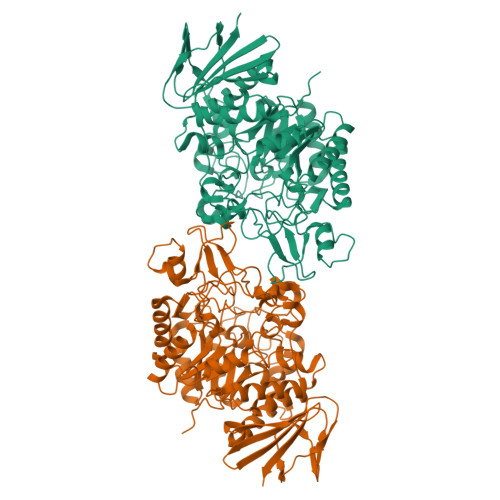
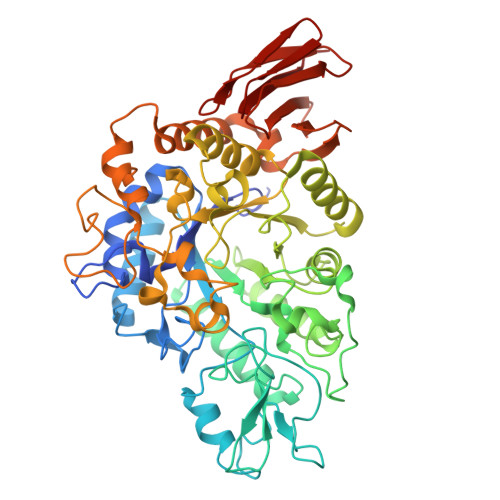
Crystal structure of alpha-glucosyl transfer enzyme XgtA from Xanthomonas campestris WU-9701.
Watanabe, R., Arimura, Y., Ishii, Y., Kirimura, K.(2020) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 526: 580-585
- PubMed: 32247611
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.03.109
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6AAV - PubMed Abstract:
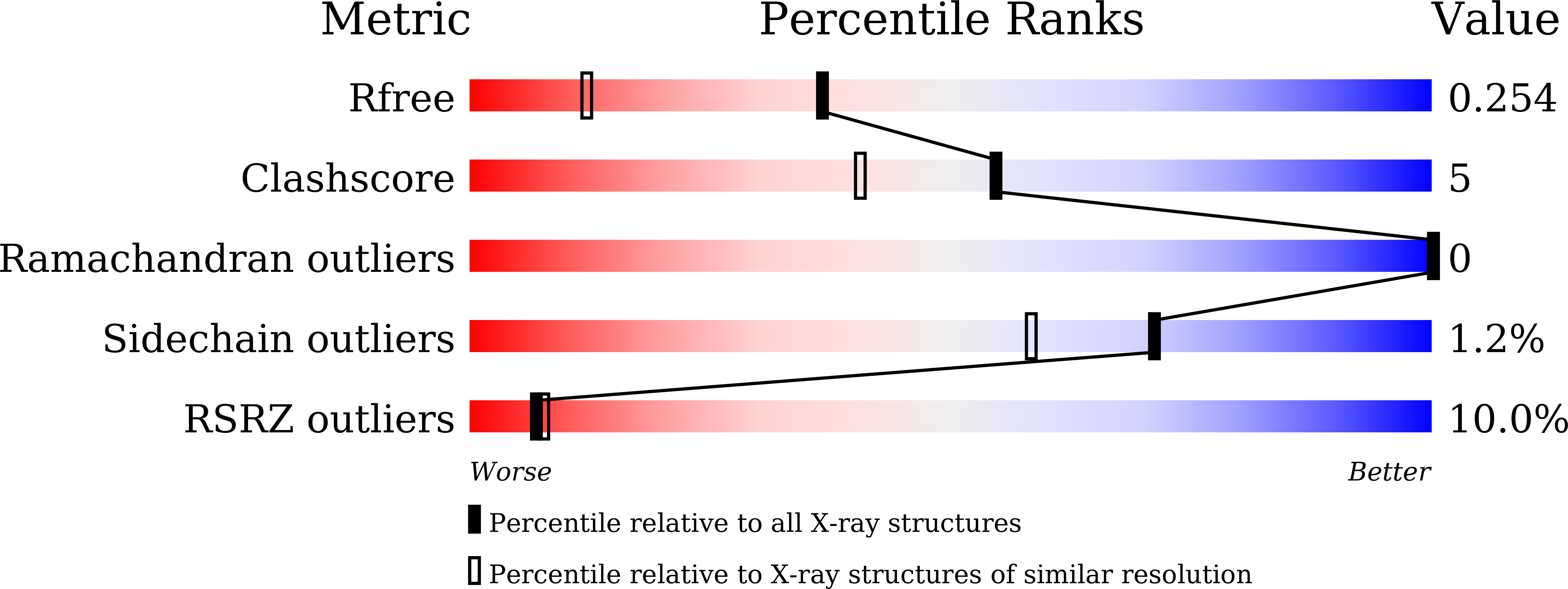
The α-glucosyl transfer enzyme XgtA is a novel type α-Glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.20) produced by Xanthomonas campestris WU-9701. One of the unique properties of XgtA is that it shows extremely high α-glucosylation activity toward alcoholic and phenolic -OH groups in compounds using maltose as an α-glucosyl donor and allows for the synthesis of various useful α-glucosides with high yields. XgtA shows no hydrolytic activity toward sucrose and no α-glucosylation activity toward saccharides to produce oligosaccharides. In this report, the crystal structure of XgtA was solved at 1.72 Å resolution. The crystal belonged to space group P22 1 2 1 , with unit-cell parameters a = 73.07, b = 83.48, and c = 180.79 Å. The β→α loop 4 of XgtA, which is proximal to the catalytic center, formed a unique structure that is not observed in XgtA homologs. Furthermore, XgtA was found to contain unique amino acid residues around its catalytic center. The unique structure of XgtA provides an insight into the mechanism for the regulation of substrate specificity in this enzyme.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Applied Chemistry, Faculty of Science and Engineering, Waseda University, 3-4-1 Ohkubo, Shinjuku-ku, Tokyo, 169-8555, Japan.