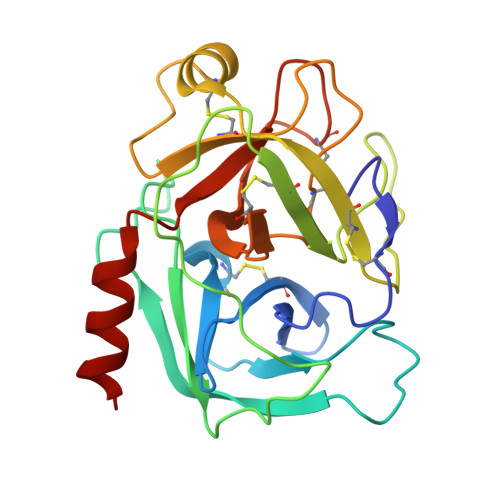
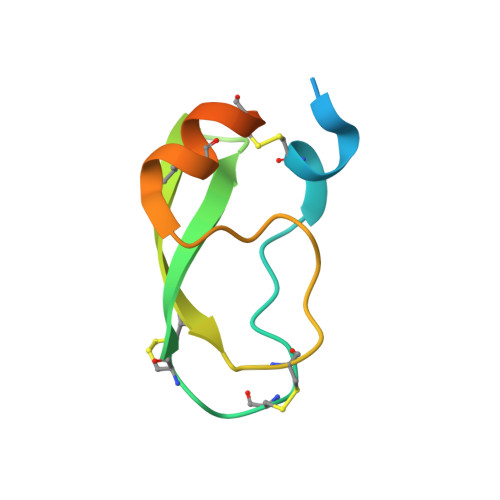
Disulfide engineering of human Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitors enhances proteolytic stability and target affinity toward mesotrypsin.
Cohen, I., Coban, M., Shahar, A., Sankaran, B., Hockla, A., Lacham, S., Caulfield, T.R., Radisky, E.S., Papo, N.(2019) J Biol Chem 294: 5105-5120
- PubMed: 30700553
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.007292
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6BX8, 6HAR - PubMed Abstract:
Serine protease inhibitors of the Kunitz-bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPTI) family are ubiquitous biological regulators of proteolysis. These small proteins are resistant to proteolysis, but can be slowly cleaved within the protease-binding loop by target proteases, thereby compromising their activity. For the human protease mesotrypsin, this cleavage is especially rapid. Here, we aimed to stabilize the Kunitz domain structure against proteolysis through disulfide engineering. Substitution within the Kunitz inhibitor domain of the amyloid precursor protein (APPI) that incorporated a new disulfide bond between residues 17 and 34 reduced proteolysis by mesotrypsin 74-fold. Similar disulfide engineering of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-1 Kunitz domain 1 ( KD1 TFPI1) and bikunin Kunitz domain 2 ( KD2 bikunin) likewise stabilized these inhibitors against mesotrypsin proteolysis 17- and 6.6-fold, respectively. Crystal structures of disulfide-engineered APPI and KD1 TFPI1 variants in a complex with mesotrypsin at 1.5 and 2.0 Å resolution, respectively, confirmed the formation of well-ordered disulfide bonds positioned to stabilize the binding loop. Long all-atom molecular dynamics simulations of disulfide-engineered Kunitz domains and their complexes with mesotrypsin revealed conformational stabilization of the primed side of the inhibitor-binding loop by the engineered disulfide, along with global suppression of conformational dynamics in the Kunitz domain. Our findings suggest that the Cys-17-Cys-34 disulfide slows proteolysis by dampening conformational fluctuations in the binding loop and minimizing motion at the enzyme-inhibitor interface. The generalizable approach developed here for the stabilization against proteolysis of Kunitz domains, which can serve as important scaffolds for therapeutics, may thus find applications in drug development.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Avram and Stella Goldstein-Goren Department of Biotechnology Engineering and the National Institute of Biotechnology in the Negev, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva 84105, Israel.