Computer-Aided Selective Optimization of Side Activities of Talinolol.
Hiesinger, K., Kramer, J.S., Achenbach, J., Moser, D., Weber, J., Wittmann, S.K., Morisseau, C., Angioni, C., Geisslinger, G., Kahnt, A.S., Kaiser, A., Proschak, A., Steinhilber, D., Pogoryelov, D., Wagner, K., Hammock, B.D., Proschak, E.(2019) ACS Med Chem Lett 10: 899-903
- PubMed: 31223445
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00075
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6HGV, 6HGX - PubMed Abstract:
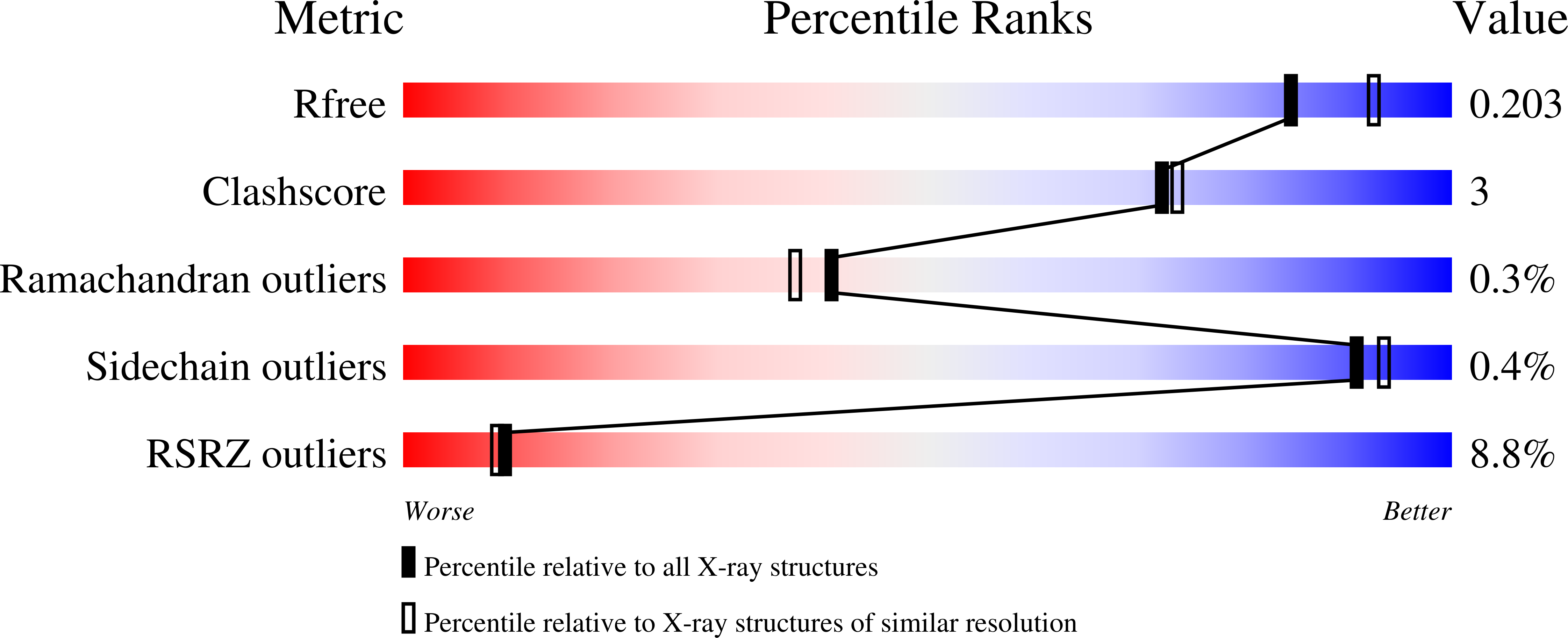
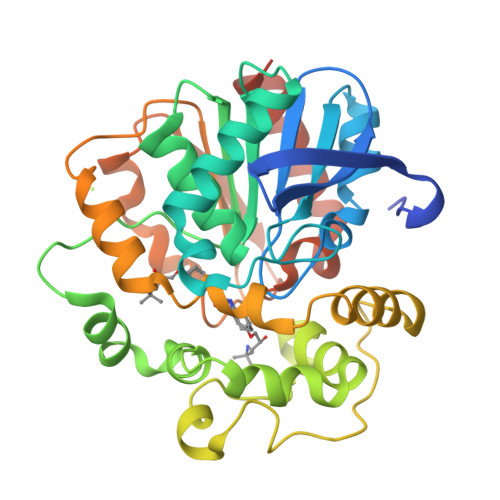
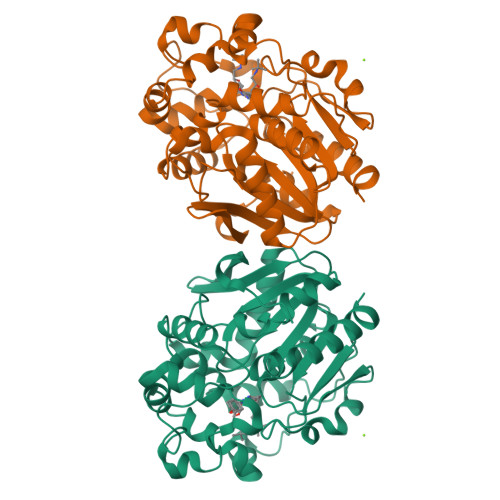
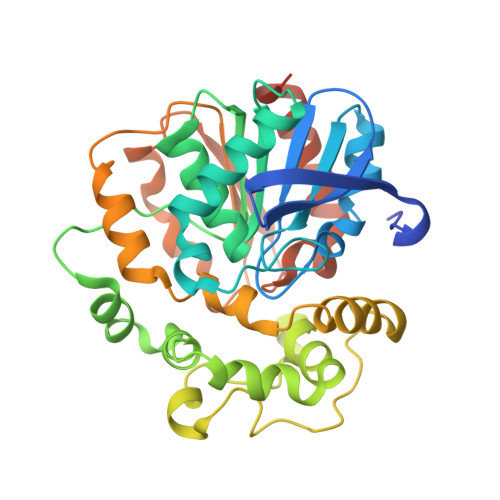
Selective optimization of side activities is a valuable source of novel lead structures in drug discovery. In this study, a computer-aided approach was used to deorphanize the pleiotropic cholesterol-lowering effects of the beta-blocker talinolol, which result from the inhibition of the enzyme soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH). X-ray structure analysis of the sEH in complex with talinolol enables a straightforward optimization of inhibitory potency. The resulting lead structure exhibited in vivo activity in a rat model of diabetic neuropatic pain.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Goethe-University of Frankfurt, Max-von-Laue Strasse 9, D-60438 Frankfurt am Main, Germany.