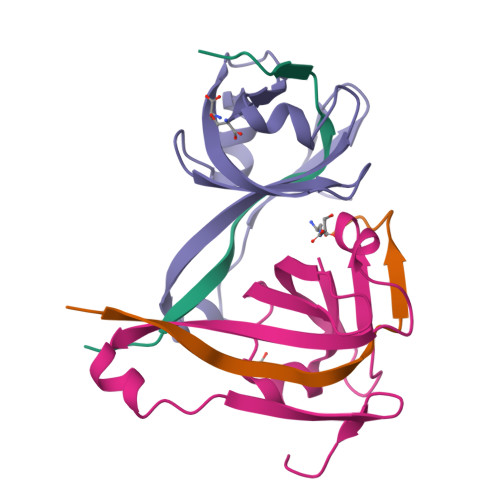
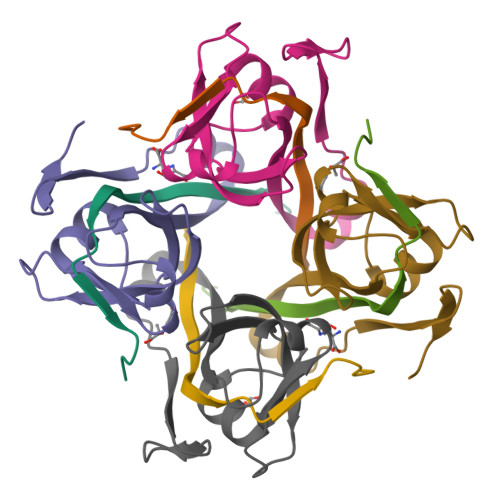
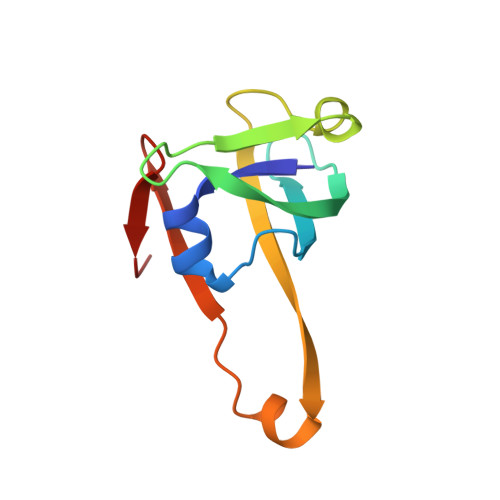
Structure and diffusive dynamics of aspartate alpha-decarboxylase (ADC) liganded with D-serine in aqueous solution.
Raskar, T., Niebling, S., Devos, J.M., Yorke, B.A., Hartlein, M., Huse, N., Forsyth, V.T., Seydel, T., Pearson, A.R.(2022) Phys Chem Chem Phys
- PubMed: 35980136
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d2cp02063g
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7A8Y - PubMed Abstract:
Incoherent neutron spectroscopy, in combination with dynamic light scattering, was used to investigate the effect of ligand binding on the center-of-mass self-diffusion and internal diffusive dynamics of Escherichia coli aspartate α-decarboxylase (ADC). The X-ray crystal structure of ADC in complex with the D-serine inhibitor was also determined, and molecular dynamics simulations were used to further probe the structural rearrangements that occur as a result of ligand binding. These experiments reveal that D-serine forms hydrogen bonds with some of the active site residues, that higher order oligomers of the ADC tetramer exist on ns-ms time-scales, and also show that ligand binding both affects the ADC internal diffusive dynamics and appears to further increase the size of the higher order oligomers.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institut Max von Laue - Paul Langevin, 71 Avenue des Martyrs, Grenoble 38000, France. tforsyth@ill.eu.