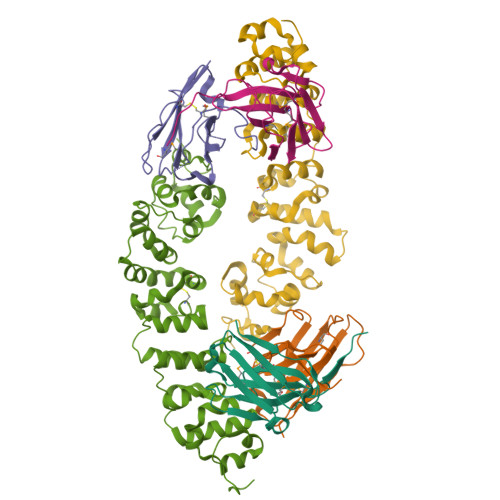
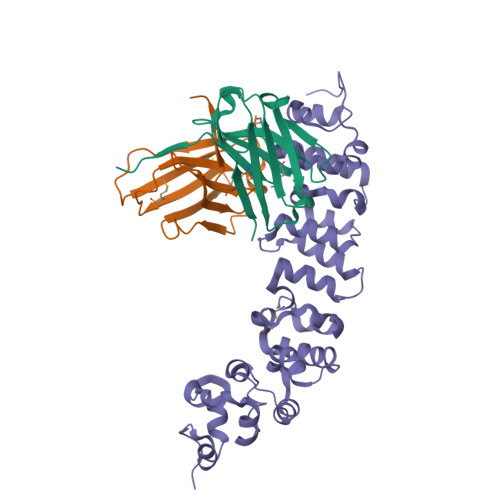
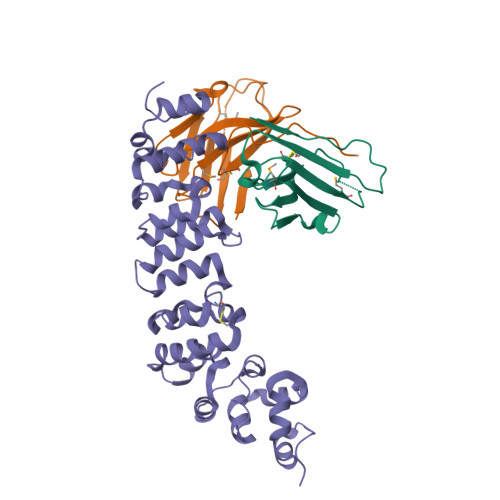
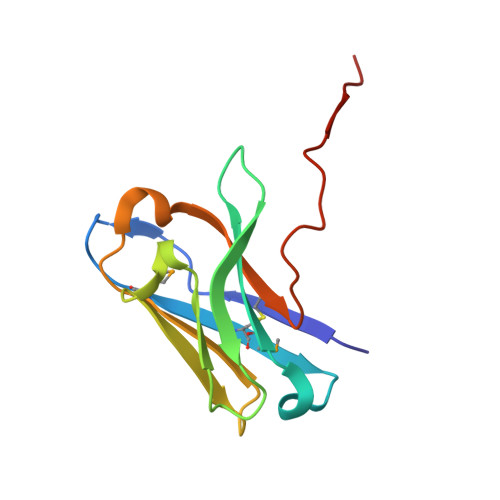
Preclinical assessment of a novel human antibody VH domain targeting mesothelin as an antibody-drug conjugate.
Sun, Z., Chu, X., Adams, C., Ilina, T.V., Guerrero, M., Lin, G., Chen, C., Jelev, D., Ishima, R., Li, W., Mellors, J.W., Calero, G., Dimitrov, D.S.(2023) Mol Ther Oncolytics 31: 100726-100726
- PubMed: 37771390
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omto.2023.09.002
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8FSL - PubMed Abstract:
Mesothelin (MSLN) has been a validated tumor-associated antigen target for several solid tumors for over a decade, making it an attractive option for therapeutic interventions. Novel antibodies with high affinity and better therapeutic properties are needed. In the current study, we have isolated and characterized a novel heavy chain variable (VH) domain 3C9 from a large-size human immunoglobulin VH domain library. 3C9 exhibited high affinity (KD [dissociation constant] <3 nM) and binding specificity in a membrane proteome array (MPA). In a mouse xenograft model, 3C9 fused to human IgG1 Fc was detected at tumor sites as early as 8 h post-infusion and remained at the site for over 10 days. Furthermore, 3C9 fused to a human Fc domain drug conjugate effectively inhibited MSLN-positive tumor growth in a mouse xenograft model. The X-ray crystal structure of full-length MSLN in complex with 3C9 reveals interaction of the 3C9 domains with two distinctive residue patches on the MSLN surface. This newly discovered VH antibody domain has a high potential as a therapeutic candidate for MSLN-expressing cancers.
Organizational Affiliation:
Center for Antibody Therapeutics, Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, 3550 Terrace Street, Pittsburgh, PA 15261, USA.